Nov 7 2012 (updated for typos)
Warning.. long monotonous blog. Sorry for the lack of connectedness, written over 7 days and my editor is rather slammed. You have been warned, so don’t complain….
Summary
- The competitive dynamics surrounding a “transaction account” (ie DDA) are shifting. For example, Retailer banking/prepaid products (Wal-Mart, Tesco, ..) offer significant fee advantages to most lower mass customers. Three party networks like Amex and Discover have unique advantages when combined with Retailers distribution/service capabilities. This means prepaid has become a disruption: a new good enough product…
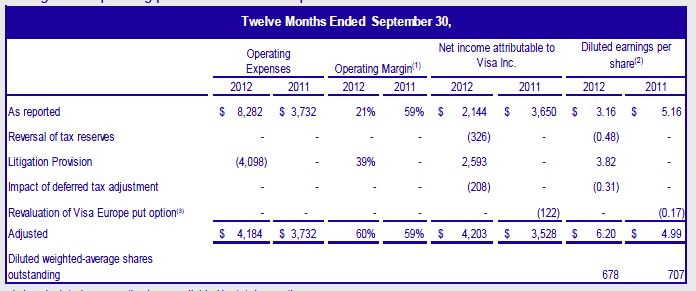
- Net interest income is 64% of total US retail bank revenues, yet the bottom four deciles of mass market customers are no longer profitable. Given that the transactional account is the #1 factor for retail bank profitability, what are implications if banks loose it?
- There is a high probability for disruptive value propositions in Payments, as advertising replaces merchant borne interchange. Payments and core banking will become a “dumb pipe” business unless Banks create value and assume a larger orchestration role. POS Payments are the central feature of a transaction account, if banks loose this relationship they will be in a poor position to orchestrate.
Does anyone else have trouble keeping up with state of the art? Who is doing what? My method of keeping up with change is to immerse myself in a given area for a day or two. It also gives me a reason to call my friends and colleagues. This week the theme is retail banking. I’ve spent too much time thinking about payments and how it relates to mobile, advertising, …etc. I thought I would dust off my banking hat and think in terms of a banker.
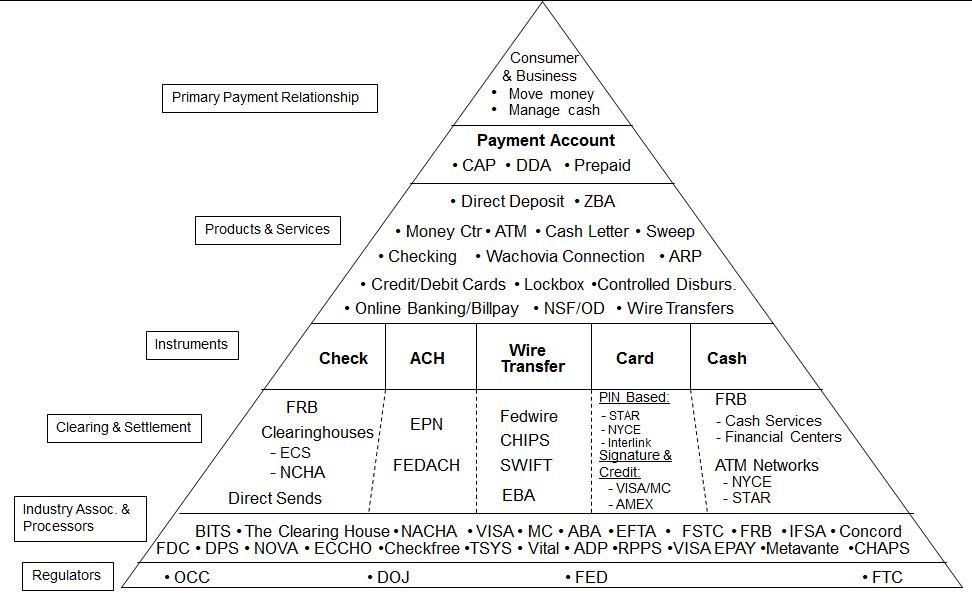
Retail Banking
I’m struck by how odd retail banking is. Why are banking services not more simple? Why do I have a separate savings, checking and card account? Why not one account? if the account runs in a arrears I pay interest and if it runs in credit the bank pays me interest? Why does a bank take 3-5 days to move money? How on earth do the banks afford all of those stand alone branches when I visit them perhaps once or twice a year? Why all of the regulation? What does my bank do for me? What problems do retail banks solve? Can someone else solve these problems more efficiently?
There is certainly no single answer. Retail banking serves many demographics, from the college student to the billionaire. Historically retail bank relationships were very important relationships, as banks only lent money to people they “knew”, based on the deposits they had. Younger consumers need to borrow, older consumers … savings. Banks focused on things like college student accounts to lock in that relationship as early as possible. Today’s modern financial markets provide for the securitization of loans, thereby spreading risk among various investors willing to assume it. Does a banking relationship matter anymore? to Consumers? to Banks?
I’m struck by how little change has occurred (in the US) on the liabilities side of the banking business? Quite frankly US consumers are treated like idiots who sacrifice “protection of capital” over risk. We now have an entire agency working to protect US consumers 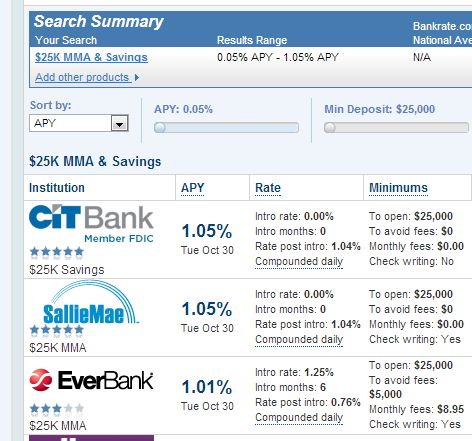 from banks.. (BTW what is predatory lending?). Other markets let consumers take on risk.. and hence have many more choices, and innovation, in savings. For example, I’m very fortunate to have worked with so many fantastic people over the years. The great thing about running Citi’s channels globally is that each and every country had a somewhat unique competitive and regulatory environment. It was like running 27 different banks. There were many different strategies for deposit acquisition, for example:
from banks.. (BTW what is predatory lending?). Other markets let consumers take on risk.. and hence have many more choices, and innovation, in savings. For example, I’m very fortunate to have worked with so many fantastic people over the years. The great thing about running Citi’s channels globally is that each and every country had a somewhat unique competitive and regulatory environment. It was like running 27 different banks. There were many different strategies for deposit acquisition, for example:
- In Spain we had a 10/2 product that paid 10% interest on deposits for the first 2 months.. then went to 1%.
- In Japan Citi leveraged its global footprint, and the poor local consumer rate environment, to create foreign currency (FCY) accounts which allowed consumers earn higher returns by assuming currency conversion (FX) risk in uninsured accounts.
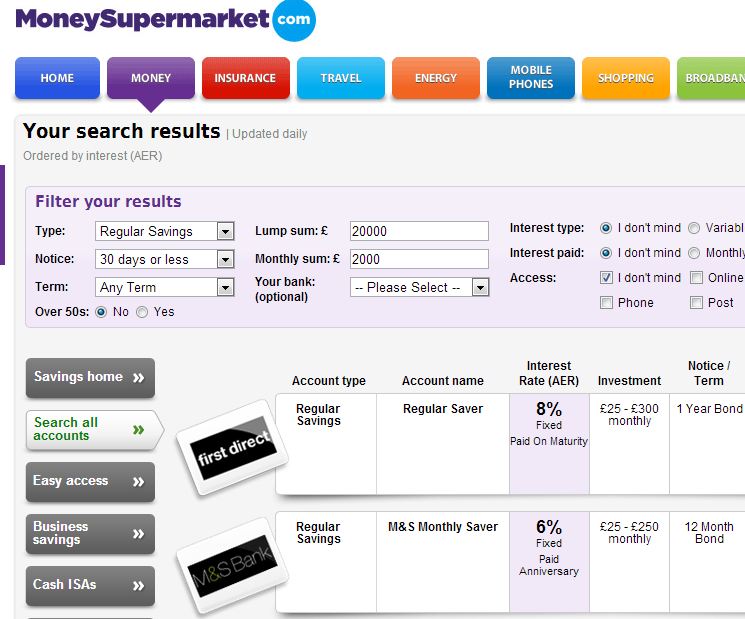
- The UK is perhaps the most competitive retail bank environment in the world. Consumers in the UK can switch banks almost as easily as changing shoes, it was thus essential to enable consumers to switch quickly and then get them into other products quickly. Take a look at today’s UK savings rates from MoneySuperMarket (8% on a fixed $30k deposit) vs the US (1.05% bankrate.com). Rate differences on this scale helped fuel the carry trade in Japan.
In the US, it is well known (inside the banking community) that banks are highly discouraged from competing on rates. Not that it matters, this amazing study by the Chicago Fed (Chicago Fed – Checking Accounts What Do Consumers Value – 2010) shows that US consumers are rate inelastic.. and care much more about fees. You have read this right, consumers don’t care about interest rates on their deposits.. which is certainly NOT intuitive. Perhaps rates are all so close to 0% that 5-10bps doesn’t matter. Or perhaps because the average US consumer does not save at all, and those that do have their money in another place.
Retail Bank Profitability. Net interest income (2011, represented more than 64% of total US bank revenues) is the rate spread between borrowing short and lending long, or more broadly the differential between asset yields and funding costs. Net interest  margins (defined as net interest income over average earning assets) were 3.6% at year-end 2011, just 11% higher from the 20-year low of 3.2% in the last quarter of 2006.
margins (defined as net interest income over average earning assets) were 3.6% at year-end 2011, just 11% higher from the 20-year low of 3.2% in the last quarter of 2006.
From DB Research
As low rates persist, loan-to-deposit spreads fall as prices adjust, and longer-term securities, held as assets, roll over to lower-yielding securities (the same holds true on the funding side, of course, helping to extend the positive impact of falling interest rates into the future). The net impact on banks’ net interest levels may be negative, though. In previous recoveries, this effect has been offset by increased loan volumes, allowing banks to return to sustainable growth levels. Furthermore, as an economy recovers, banks may quickly benefit as short-term assets roll over at higher rates
To summarize: Bank net interest income is important (64%), and falling. Banks have had a key revenue source taken away from them (Debit interchange) and are also facing another merchant led suit on credit card interchange. Bank brands and reputations are on a steady downward trend. Consumers don’t care about rates, but react strongly on fees. … A new regulatory agency to protect consumers is just now forming and looking to make its mark. What are banks to do?
Transaction Account
What is the purpose of a bank provided transactional account today? Well certainly our mattresses are a little less lumpy, and the relationship factors have largely gone away. So what is left? Transactionality?
The banks have long recognized that the transactional account is the #1 factor driving a consumer relationship. Virtually every other banking product and service hangs from this account. Most retail banks view direct deposit (internationally known as Salary Domiciliation or Sal Dom) as the key indicator of the transactional relationship. Consumers have limited “energy” to connect to more than one network (as outlined in followed my previous blog on Weak Links).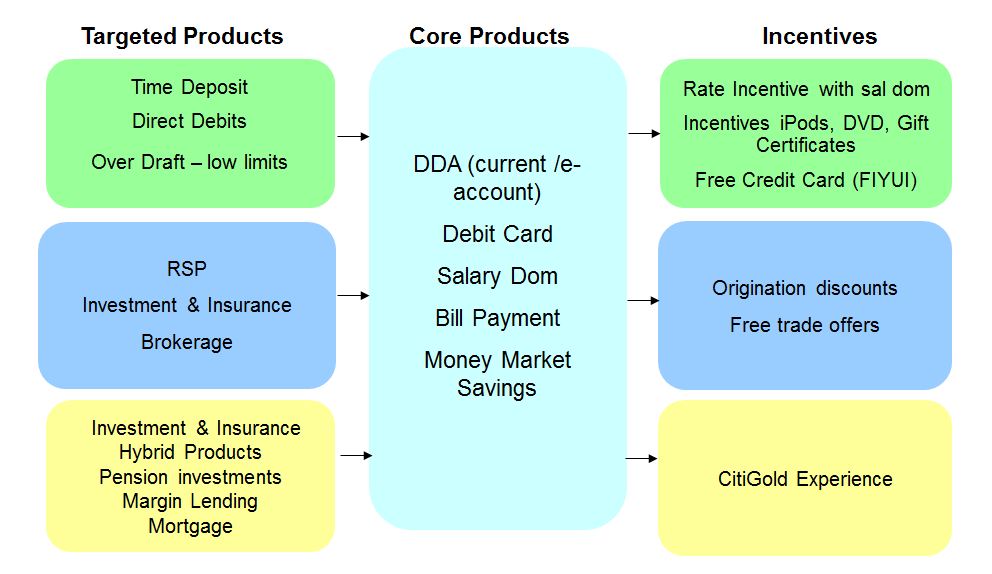
This financial supermarket concept, authored by Sandy Weill and John Reed, has not exactly been a slam dunk success. Nonetheless every retail bank starts selling with a checking account, even if nothing else is attached. What are the key factors influencing the selection of a transactional account?
- Why are deposits important to banks?
- Driver of overall relationship à Customer Net Revenue
- Liquidity ratio ->Risk ->Agency Rating -> Capital Costs
- How do consumers select a bank?
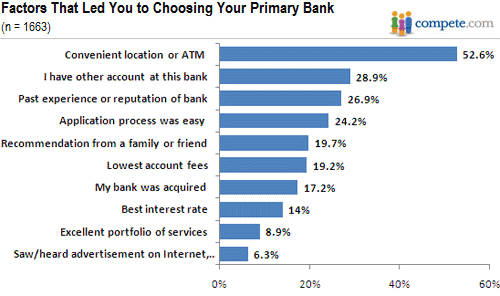

The public compete data above is completely consistent with previous proprietary studies I’ve commissioned. Consumers tend to pick their bank based on how convenient the branch and/or ATM is.
Is there something fundamentally changing? What if consumers don’t visit a branch… or no longer use cash? Are there new value propositions? Where will consumers (and their deposits) go?
Recent market developments/Announcements
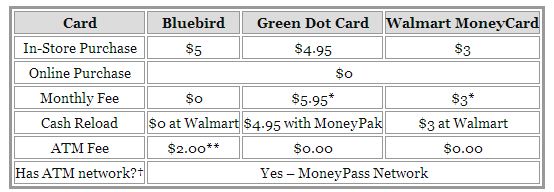
The Amex Bluebird product is revolutionary in terms of fees. It is the lowest cost reloadable card in the market today. Beyond the product, I’m even more impressed with WalMart’s business strategy here. They seem to be willing to break even on payments/banking in order to win the overall consumer relationship and increase foot traffic and loyalty in their stores. Take a look at the suite of products offered by WalMart. While banks are pushing out the bottom forty percent of mass consumers, WalMart has made a bet that it cannot only serve them, but do so profitably.
There are many different types of pre-paid cards (more below), however most are not regulated as bank accounts. In almost every geography, consumer deposits (interest bearing, insured) are regulated because they drive both bank liquidity (which drives lending and cost of capital) and profitability. Remember before capital markets existed to securitize assets (loans) retail banks could only lend to the extent of their balance sheet (deposits). Consumers put their money with banks in order to earn interest (the carrot) with the downside of fees on usage (the stick). In the US consumers are beginning to ask themselves “is the carrot big enough”?
In emerging markets many banks have a poor reputation, additionally access to legal resources are limited, as are consumer protections. How would you feel if you showed up to your bank for a withdrawal and your bank said “sorry your money is gone” and you had no recourse? This dynamic has propelled other banking models in emerging markets. For example my friend Nick Hughes and his Vodafone/Safaricom team created MPESA in Kenya which provided enormous value to consumers. However MPESA caused an apoplectic reaction from the banking regulators as 10% of Kenya’s GDP sat in a non-interest bearing Vodafone owned settlement account. MPESA therefore impacted bank liquidity (IF the funds would have gone into a bank account as opposed to just M1/cash). Visa and MA have worked hard to try to make prepaid the underlying account for mobile money in emerging markets, to very little avail. The problem is not connecting people to the V/MA network.. and giving balances to an approved bank. The problem is first transferring money to entities currently not on any network, then paying a very small number of billers. 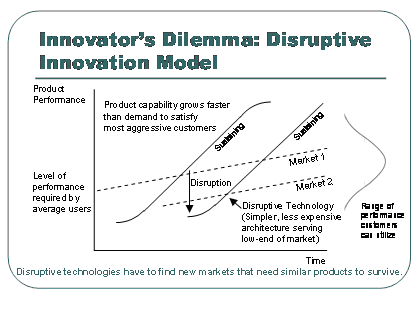
Why are consumers defecting in the US? Ernst and Young just published a phenomenal global study on this subject. The result of their analysis was that consumer confidence in banks is degrading. E&Y outlined a call to action by banks: reconfigure your business models around customer needs. My hypothesis is that consumers have reached a tipping point where they view banking services as commodities… In the UK, this is already well established.
Prepaid
I haven’t spent much time thinking about prepaid cards so I thought it was time to refresh myself, particularly in light of MCX and the prospect of retailers acting as Banks.
From the US Fed
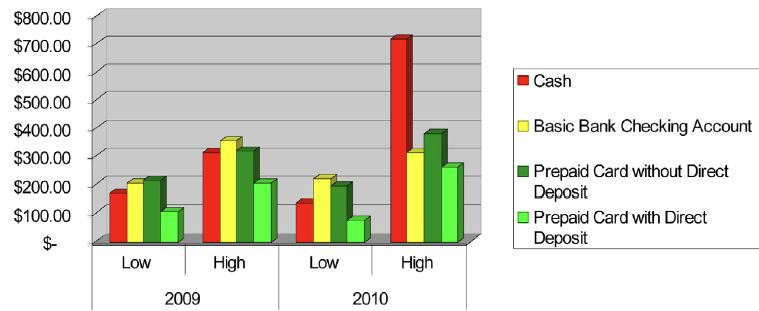
Prepaid cards offer much of the functionality of checking accounts, but that does not mean the underlying economics are the same. A typical prepaid card in the data is active for six months or less, a small fraction of the longevity seen with consumer checking accounts. As a result, account acquisition strategy and the recovery of fixed and variable costs are likely different than for checking accounts. …. prepaid cards with [direct deposit are uncommon but] remain active more than twice as long and have 10 times or more purchase and other activity than other cards in the same program category. As a result, these cards typically generate at least four times more revenue for the prepaid card issuer
Similarly Pre-paid cards also face a complex web of regulation (See Philadelphia Fed Paper 2010), across 31 different types of cards.
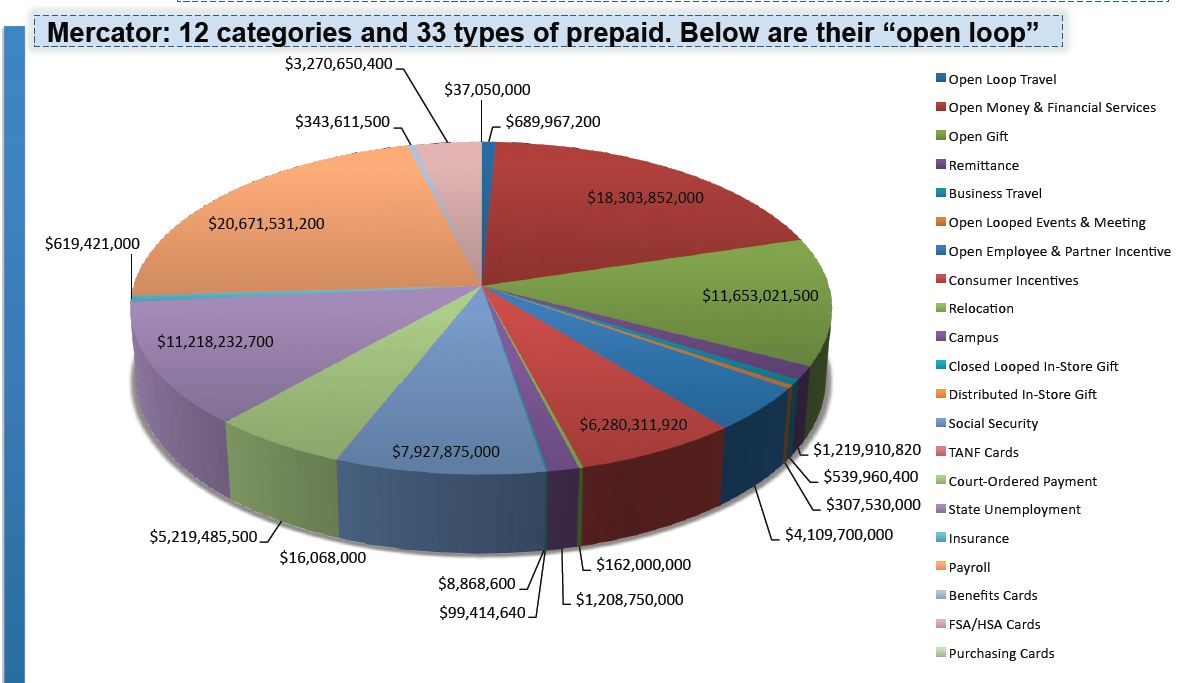
31 types of cards? Did anyone else realize the diversity here? Wow… For the sake of this blog, let’s focus on reloadable (GPR) open loop cards (references to prepaid below are on this card type only). It would seem that GPR pre-paid is following the general disruption pattern of serving a lower tier of the market at a more attractive price point. According to Mercator, In 2009, consumers loaded $28.6 billion onto prepaid cards. By 2015, prepaids will hold $168 billion.
Last month’s WSJ ( Prepaid Enters Mainstream) outlined this dynamic
Traditional leaders in GPR pre-paid have been Green Dot, NetSpend, . The Durbin amendment exempted most prepaid cards. This means that pre-paid is largely example from the Durbin interchange restrictions… (with several conditions). Thus the business case for pre-paid is rather strong, and Banks themselves are assessing if they can make this the new “starter” account (ex Chase Liquid). However Three Party Networks (Discover and Amex) have a significant advantage.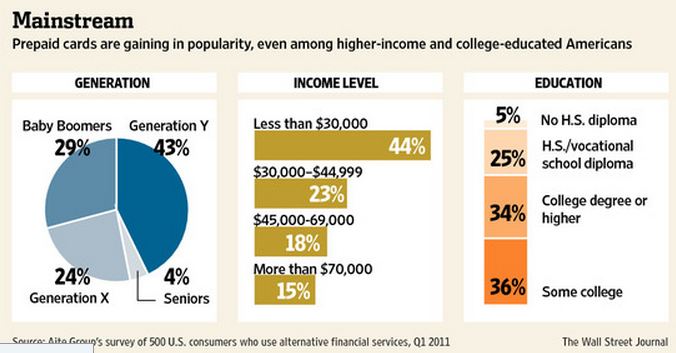
From Digital Transactions, March 2012
While the Federal Reserve’s rule implementing the Durbin Amendment has its greatest effect on traditional debit cards, it affects prepaid cards too, especially its provision that banks’ prepaid cards can avoid Durbin price controls only if cardholders can access the funds exclusively through the card itself. That provision thwarted banks’ efforts to make prepaid cards more like demand-deposit accounts and led them to scale back or end bill payments through prepaid card accounts.
But American Express and Discover are not subject to Durbin’s controversial provisions, Daniel and Brown noted. Both companies are so-called “three-party” payment systems that function both as merchant acquirer and card issuer. In contrast, Visa and MasterCard debit and prepaid cards are part of “four-party” systems in which the issuer and acquirer are usually different companies and rely on the Visa and MasterCard networks to route transactions among them. The Durbin Amendment exempts, or “carves out” in industry parlance, three-party networks from its provisions, including interchange regulation.
“There’s no restriction on what AmEx can pay itself” for prepaid card transactions, said Brown. Thus, AmEx and Discover have a new opportunity to grow their prepaid businesses, the attorneys said.
Clearly Discover (DFS) and American Express (Amex) have an opportunity to “Kill” prepaid cards, what are they missing? Physical distribution, service and reach in the mass market. These are the very things that retailers like WalMart can provide, and in fact economically benefit by providing them.
As you can tell, regulations are driving the business models here. Most large US retailers leverage a fantastic team of attorneys from Card Compliant that specialize exclusively in prepaid cards (run by my friend Chuck Rouse). WalMart’s move to Amex is brilliant both from a regulatory and business model perspective. 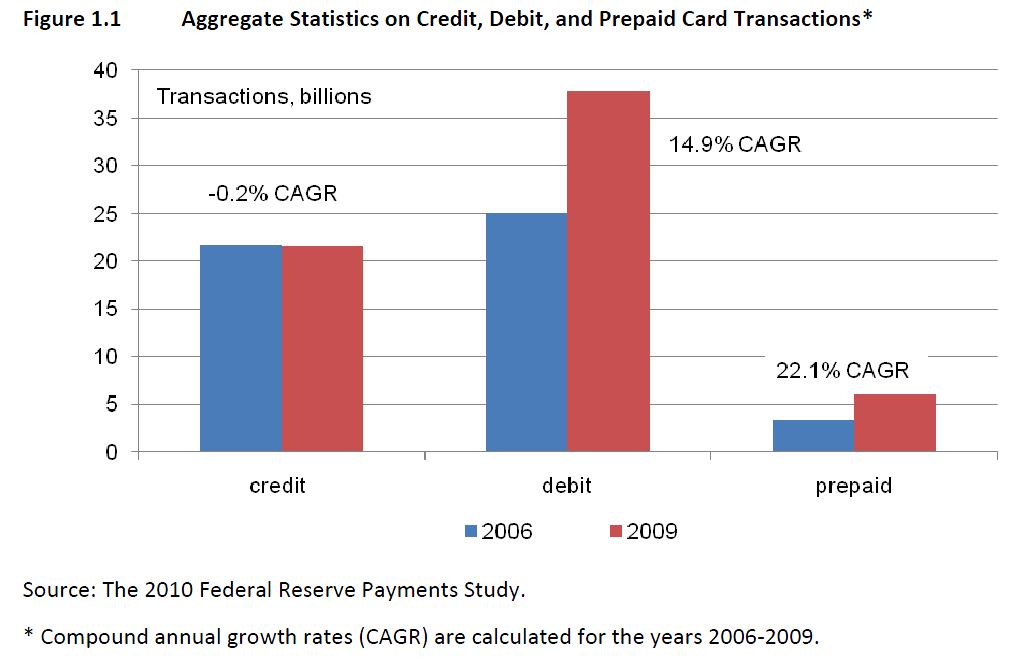
Today’s pre-paid dynamics may be the tipping point by which 3 party networks begin to overtake V/MA in growth. A trend that will accelerate when other business models require “control”. This next phase will be centered around merchant/consumer transaction data, which will begin to unlock the advertising revenue pool, which is almost 4 times larger than that of payments.
Payments and core banking will become a “dumb pipe” business unless Banks create value and assume a larger orchestration role. POS Payments are the central feature of a transaction account, if banks loose this relationship they will be in a poor position to orchestrate. 4 party networks are very, very hard to change.
I see a battle where 3 party networks work to branch into orchestration and advertising, and existing orchestrators (ie Apple/Google) integrate legacy dumb pipes (payments and telecommunication) to deliver value to the consumer. What do consumers value today? This is the call to action for bankers… who are not always the best at creating alliances.
Here is one idea, focus on trust and helping consumers solve problems they don’t face frequently. For example,
- Make financial planning easier and less of a sales job.
- Help manufactures and retailers connect to target consumers.
- Become a buyers agent?
- Help navigate the college application and loan process,
- Help buy a new car for the lowest possible price…
I know this is not a clean finish.. but that’s all the time I have.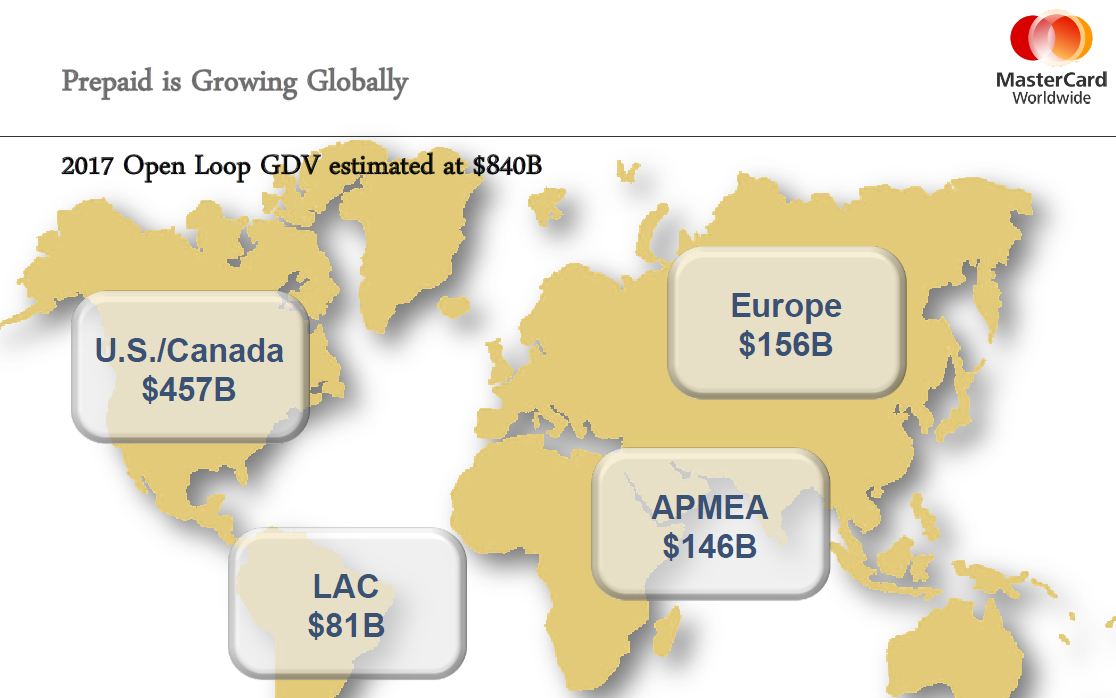
References
Thank you Kansas City Fed for the fabulous brief from the: CONSUMER PAYMENT INNOVATION IN THE CONNECTED AGE. Bill Keeton and Terri Bradford were nice enough to invite me, but unfortunately I couldn’t attend. In my last visit to the KC fed we spoke about future payments types, but we also spent quite a bit of time discussing where mass market consumers will go if banks view the bottom 4 deciles of retail banking as unprofitable (according to proprietary McKinsey Study). Today I thought I would pull together a compendium of my learnings on retail deposits, MSBs and pre-paid… the “transaction account” by which payments flow.