2 Oct 2011
Loads of new press out related to NFC
– ABI research estimates $100B GDV by 2015 (yeah.. and pigs fly)
– EMVCo 47 page report on technical standards for contactless payments
– Visa’s new mandate to retailers.. EMV (+ NFC) by 2015 or merchants bear the fraud loss
– PayPal dissing NFC (today)
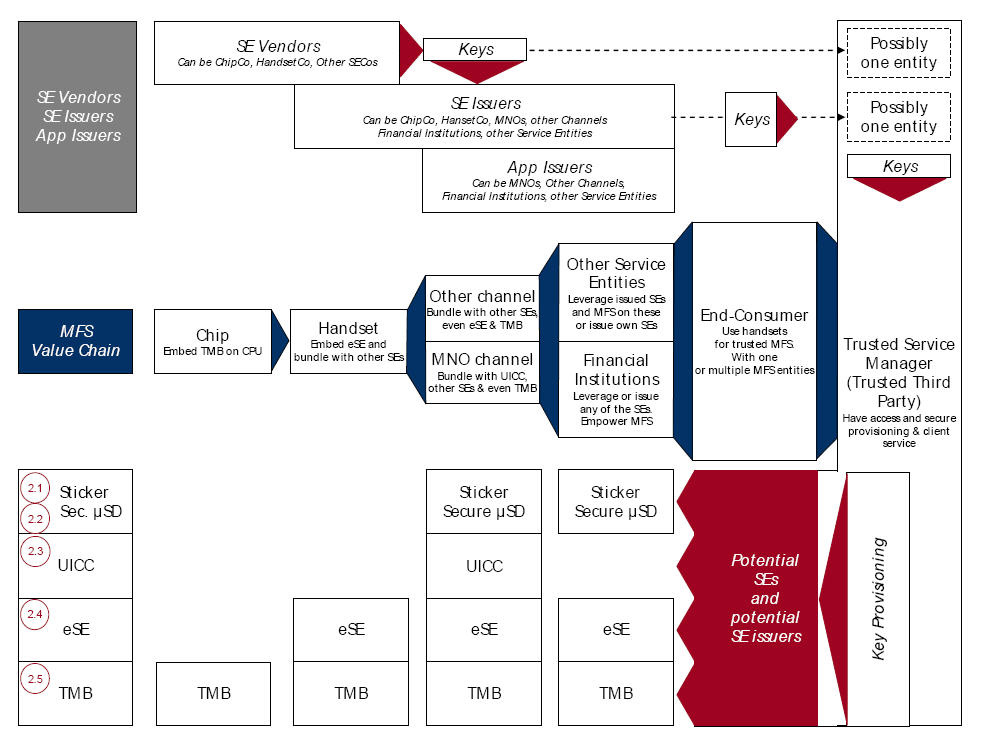
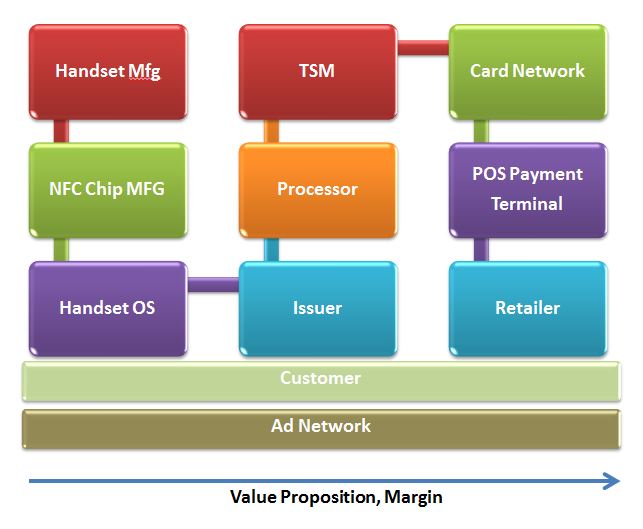
Having been the first to break the news on ISIS in 2009 (Although I was wrong on Visa involvement… it was Discover), perhaps I should be the first to predict its demise.. UNLESS something big changes. The problems with mobile money is 5% technology, 95% business model. Take a look at my diagram below… 11 parties that need to execute on a clear value proposition… No wonder MNOs like Verizon are hedging their bets, creating alternate payment solutions (see my Payfone blog).
What company can invest in something it can’t control? That has a value proposition that is unproven? That requires collaboration with competitors? That customers may not want or pay for? Please someone give me an example…
Payments (in isolation) adds very little value to an overall commerce value proposition. Did you buy your big screen because they took Visa? No.. you chose your big screen TV because it was the right model for you and you expected the merchant to offer you payment alternatives. Most of you reading this would probably have accepted 2-3 options.. The most important value proposition for any commerce network is targeted to the retailer.
ISIS started off with a great retailer value play (see my previous pro forma financials), the Barclays/Discover instrument would have been a winner.. credit the involvement of WalMart with the strategy of ISIS here.. as WMT was key in ISIS’ participation and Abbott’s hiring (former GE Money Exec… GE services WMT’s pre-paid cards). But the card networks found a way to put the screws on… and destroyed a very innovative product.. and their merchant value proposition along with it. To compensate for the ISIS 50 bps “carrot”, Visa has constructed an EMV stick (see above) to force merchants to accept EMV.. (and in essence NFC). Retailers are frequently assumed to be a bunch of back water idiots.. as a former banker I admit my mistakes… this simplified view of retail could not be further from the truth.. Retailers are on the cutting edge of competition. Competition drives data based decisions, customer centricity, daily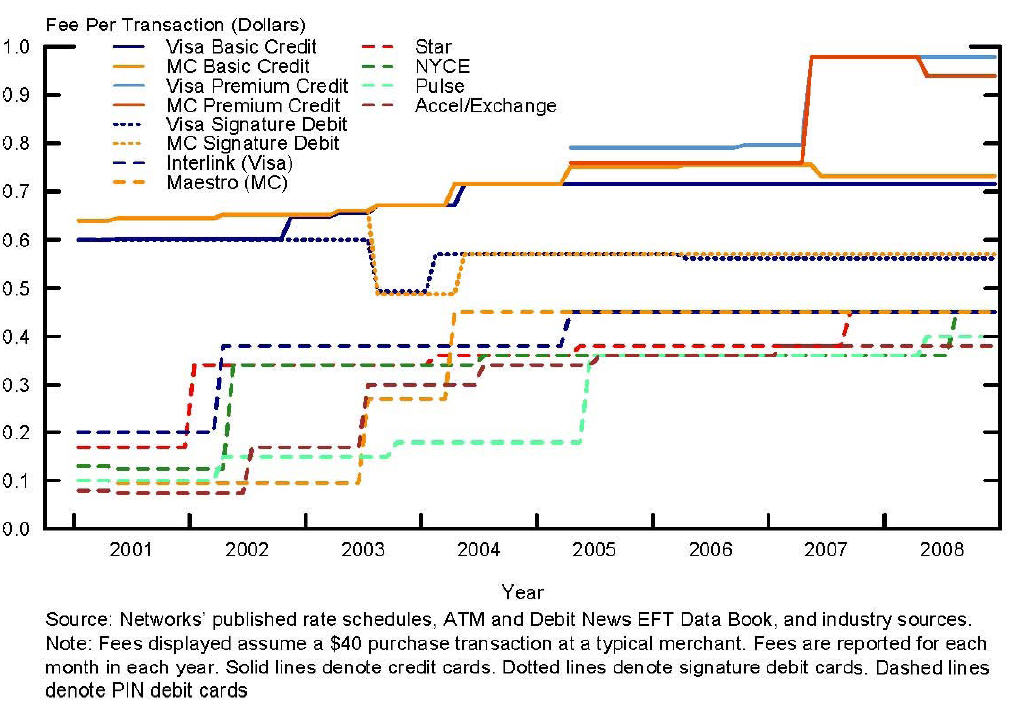 focus on margins (as they are razor thin) and a toughness matched only in professional sports. Retailers know customers like few others.. Few names generate a more intense visceral reactions among retailers than Visa and Mastercard. Today’s card networks are no friends of retail. It was no single factor.. but rather decades of choices all made to favor one group: issuers.
focus on margins (as they are razor thin) and a toughness matched only in professional sports. Retailers know customers like few others.. Few names generate a more intense visceral reactions among retailers than Visa and Mastercard. Today’s card networks are no friends of retail. It was no single factor.. but rather decades of choices all made to favor one group: issuers.
In this environment.. which retailers do you think are anxious to assist Visa and MA with a new generation of payments that is more expensive than what they have already? Specifically, NFC is a credit card transaction.. carrying a 300-350bps rate. Although there is nothing to prohibit NFC based debit card.. there are no banks (other than Discover/Barclays) that have stepped into this debit space. Visa and MA see NFC as the next great driver of CREDIT card transaction growth. Thus, Visa’s EMV moves are meant to accelerate this. Currently MNOs (and ISIS) are being taken for a ride by the banks as a tool to drive this.
Google was brilliant to include a pre-paid card in their wallet to balance the options for consumers, ISIS will likely do the same. But the conundrum faced by ISIS is that there is no revenue for the ecosystem above without credit card fees and no merchant value proposition WITH them. The answer of course is for NFC to develop a new revenue model and value proposition (see my Googlization post), but building an Ad network is no easy undertaking.. and it even more complex for ISIS since their owners are each undertaking the development of separate ad network initiatives (VZ has equity stakes in Cellfire, mphoria, and a 200 person team).
Now add this dynamic to the complexity of executing against a business model (any business model) across 9+ parties and you see the NFC business enigma. As I stated in Nov 2009, MNOs know how to be successful in payments. ATT ran the most successful private label card of all time.. they have tremendous (non monetary) tools to incent consumer behavior (ex think free unlimited data). 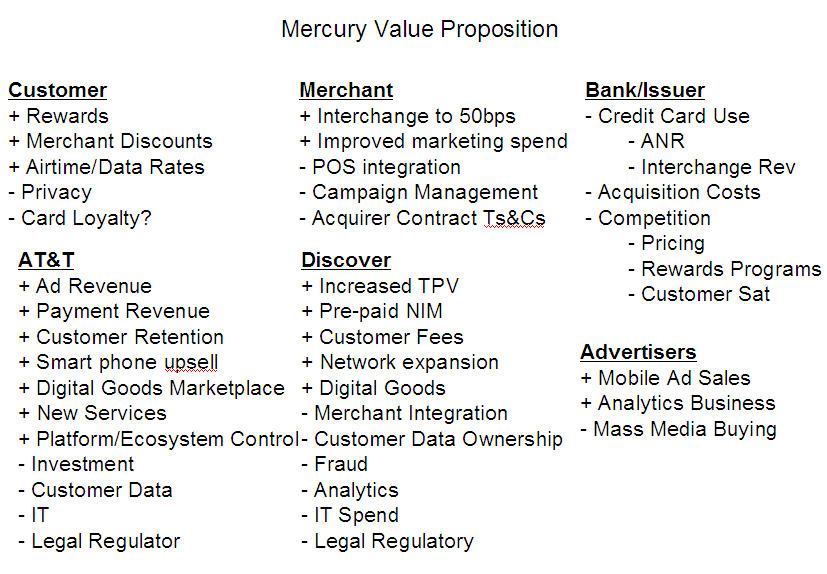 Unfortunately they don’t have experience in working with retailers.. or in orchestrating commerce interaction. ISIS will execute on the charter given to them.. but that does not mean it will be successful. Having a functioning NFC wallet does not mean that anyone will use it. Particularly if it is disconnected from everything else that I do use (mail, maps, search, Android Marketplace, …). This is where Google excels. Not only does Google have the best engineers on the planet, they have the best retailer relationships AND customer relationships.
Unfortunately they don’t have experience in working with retailers.. or in orchestrating commerce interaction. ISIS will execute on the charter given to them.. but that does not mean it will be successful. Having a functioning NFC wallet does not mean that anyone will use it. Particularly if it is disconnected from everything else that I do use (mail, maps, search, Android Marketplace, …). This is where Google excels. Not only does Google have the best engineers on the planet, they have the best retailer relationships AND customer relationships.
Remember NFC was a construct of the NFC Forum, a group formed in 2004 to design a new protocol that could be controlled by MNOs and Handset MFGs. Again.. it was designed for CONTROL…. ISIS is proving that it has fantastic facilities for control of the secure element, particularly in the US where post-paid handsets are subsidized. What ISIS fails in is a consumer and retailer value proposition. If they do not find a way to work with other participants, the window of opportunity for NFC will fade. I give ISIS 12 months…
What are the alternatives to NFC? I told a start up CEO this week that NFC is but one alternative to identifying someone at a POS. I could use a card, GPS location, biometric, .. just about any form factor to achieve the same thing (as an example look at Square’s Card Case, or VZ/Payfone). Also.. we all know that locking card information inside the phone is just plain stupid.. It’s how Microsoft worked before the internet existed.. today we are in the world of cloud computing where information lives on the cloud.. (See my previous blog)
Messages for ISIS
- Improve your retail value proposition
- Get the carriers aligned on the “SUPER” Value proposition… or you will have a wallet that functions.. but no one wants. Take a look at Enstream in Canada for a use case here. Zoompass was the precursor to ISIS….
- Move beyond control focus to VALUE focus. Build partnerships which will help you orchestrate commerce. Of course this is not in your charter.. and very, very hard for competitors to do… so this will be a driver in your demise.
- You will not get the data on every transaction occurring on the phone.. so give it up now. Both ATT and VZ are ISPs as well as backbone providers, do you keep every piece of data flowing through the internet? Your plan here is FUBAR…
Message for Retailers
- NFC terminals will only drive expense growth until there is a consumer value proposition. The only entity that is coming close here is Google. Google does not care about transaction revenue.. they care about value creation.. this is a retailer friendly structure.
- Delay your EMV/NFC plans.. The big issuers will not be reissuing cards.. so even if Visa follows through on the liability shift it will only be for cards that could have been validated.. So your risk is of fake EMV cards.. Perhaps if you see an EMV card you just ask for a customers ID.. sound rather simple…?
- Ask very simple questions and get clear answers: how will this deliver incremental sales? What kinds of customers will be using this?
My prediction? ISIS and MNO initiatives will be successful in Transit. Retailers will migrate to a new commerce network that steers clear of Visa and MA.

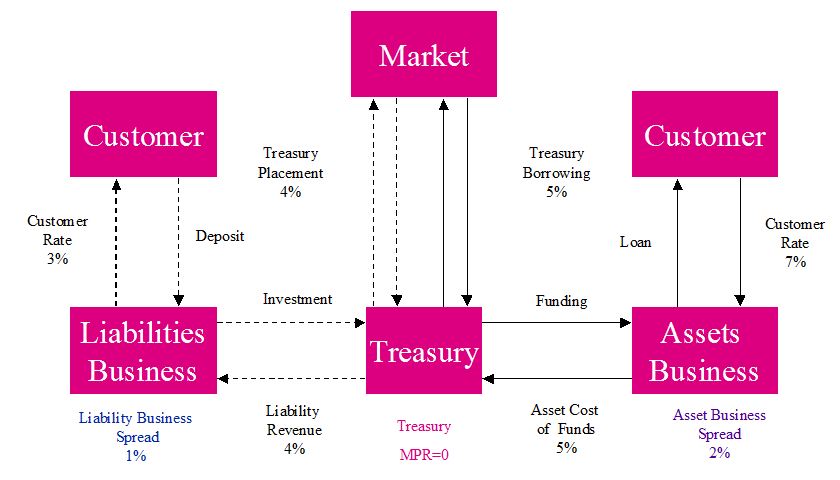
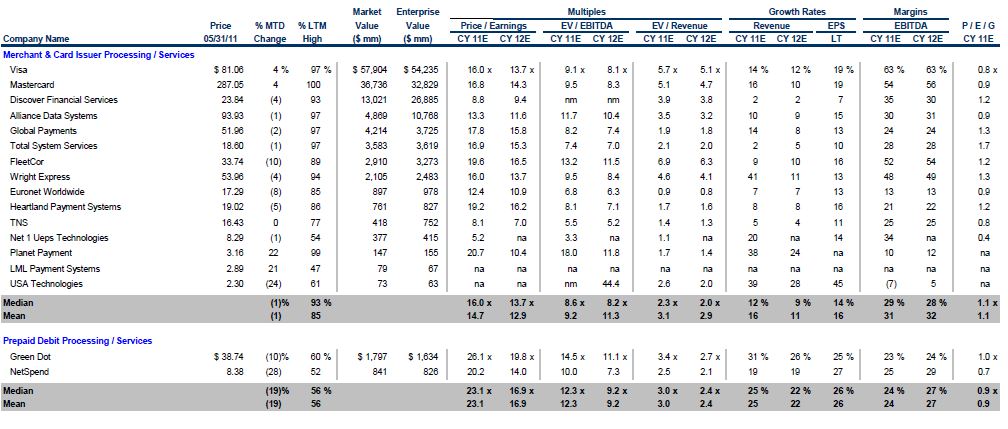

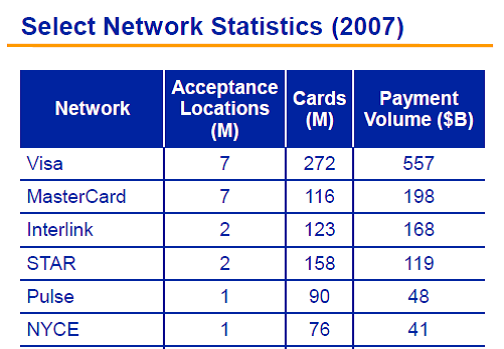
 The litmus test for disruption involves delivering service in a substantially different cost structure. A key example is delivering simplified “good enough” product to a demographic that is “over served” by existing providers. From my (very limited) purview, there seems to be 2 core
The litmus test for disruption involves delivering service in a substantially different cost structure. A key example is delivering simplified “good enough” product to a demographic that is “over served” by existing providers. From my (very limited) purview, there seems to be 2 core