8 Dec 2011
I’ve been reading some off beat stuff lately. One book “Weak Links: Stabilizers of Complex Systems from Proteins to Social Networks” was very thought provoking. As Mark Stefik (PARC Fellow) said ‘Something magical happens when you bring together a group of people from different disciplines with a common purpose.’ The combination of people, experience and approaches often leads to unexpected consequences.
As an engineer I like to solve problems.. I usually learn more from mistakes than I do from successes… but it is the learning that is fun. As an investor and entrepreneur I don’t like making mistakes… my preference in the start up environment is to have the learning cycle counted in minutes and days (vs customers and capital). I was speaking with a US Central Banker last month and the concept of “openness” was discussed. A hypothesis was laid out by the Fed “Mobile payments are not taking off because of a lack of common standards”. The Fed team is very good, the best way to encourage a good dialog is to lay out something radical; as for this hypothesis I disagreed completely. As stated in my numerous blogs: history has clearly showed that closed systems must form before open ones. I also told the Fed that the problem in US mobile payment IS NOT lack of standards but lack of a value proposition to consumers and retailers. In other words existing payment instruments solve all of my problems.. mobile payment simply does not add additional value (in isolation) compared with existing products (See Mobile Advertising Battle). In order to stimulate a change in behavior (merchant and consumer) there must be a strong value proposition. Two years ago I discussed the implications for broad payment standards in SEPA: Chicken or the Egg and in March of this year I outlined how SEPA has depressed payment innovation in the EU.
Given all of the chaos in NFC at the moment, I woke up this morning asking myself what is the “right amount” of openness and standards? How do successful networks form and mature? What are successful “open” networks? What is the first “open” standard you think of ? TCP/IP? Linux? Java? RosettaNet? EDI? Open Network? Internet? GSM? US Interstate system? SEPA? The Weak Links book opened my eyes to many new concepts, one was on how affinity influences network creation, and another on how few open networks exist in Nature. Networks form around a function and open networks are not necessarily the most efficient.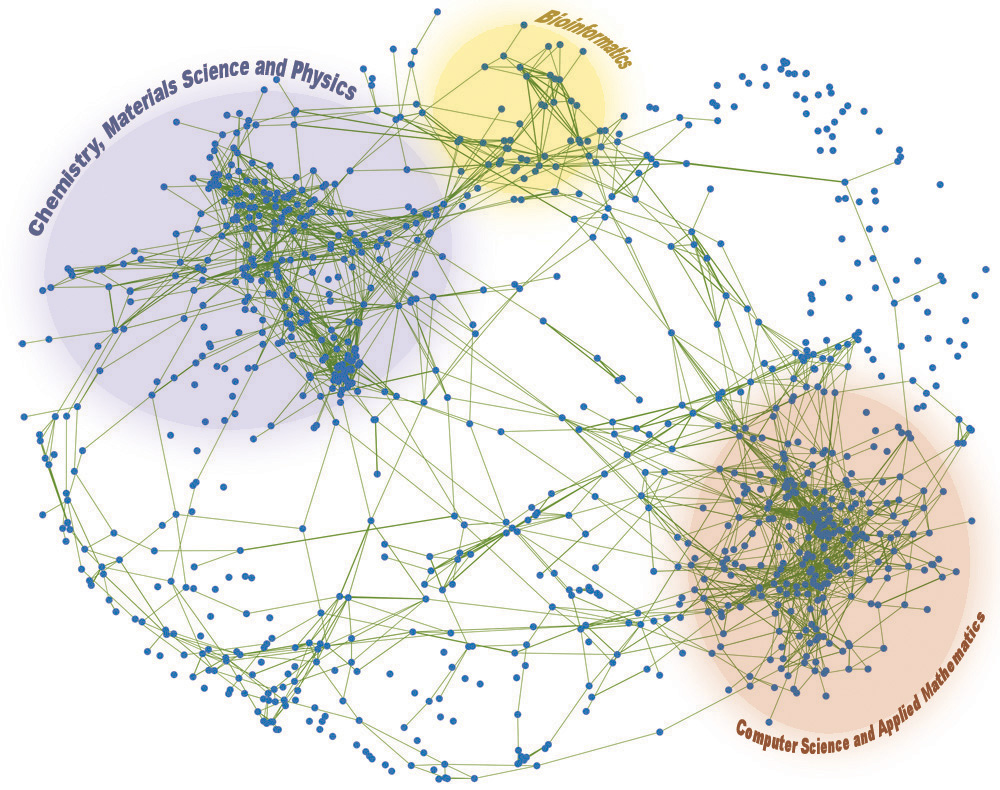
Scale-free distribution (completely open networks) is not always the optimal solution to the requirement of cost efficiency. .. in small world networks, building and maintaining links between network elements requires energy…. [in a world with limited resources] a transition will occur toward a star network [pg 75] where one of a very few mega hubs will dominate the whole system. The star network resembles dictatorships in social networks.
The network forms around a function and other entities are attracted to this network (affinity) because of the function of both the central orchestrator and the other participants. Of course we all know this as the definition of Network Effects. Obviously every network must deliver value to at least 2 participants. Networks resist change because of this value exchange within the current network structure, in proportion to their size and activity. Within the EU, SEPA undertook a rewrite of network rules and hoped that existing networks would go away or that a new (stronger) SEPA network would form around its core focus areas (SCT, SDD, SCF, ..). It was a “hope” because the ECB has no enforcement arm. In other words there was a political challenge associated with ECB’s (and EPC specifically) ability to force an EU level change on domestically regulated banking industry.. given that SEPA rules destroyed much value in existing bank networks, the political task was no small effort. We have seen similar attempts (and results) when governments attempt to institute major change in networks (Internet NetNeutrality v. Priority Routing, US Debit Card Interchange, …)
Mobile Payments Standard?
If we take a look at today’s payment networks what are the biggest problems to be solved? I have a perspective, but its certainly biased. How about payment routing and speed? These seem to be common merchant and consumer concerns. Keeping with an internet analogy, can you imagine if there were no DNS servers to route IP traffic? Every router would have to keep the directory for the entire internet not only of the final destination, but also the most effective route to forward traffic. What if the internet were not indexed? No ability to find information (thanks Google for fixing this). In the payments environment, the central assets of Visa and MA is 1) A Directory and 2) the rule that EVERY participant must route traffic through them (with a new PIN debit exception in US).
Outside of card transaction’s banks maintain their own directory for routing retail and commercial payments; this is called “least cost routing”. A key bank service I  would propose (note: I’m not the originator of this idea) is a universal directory service mapping e-mail, phone and account numbers. In Australia, the banks have this today run by my friends at Cardlink and completed under project Mambo. In the US, The Clearing House (TCH) has had the UPick service completed for a number of years.. without much interest.
would propose (note: I’m not the originator of this idea) is a universal directory service mapping e-mail, phone and account numbers. In Australia, the banks have this today run by my friends at Cardlink and completed under project Mambo. In the US, The Clearing House (TCH) has had the UPick service completed for a number of years.. without much interest.
My thought here, is that rather than facilitate a EU mistake in mandating a change in all rules.. decrease the switching costs between networks so that market forces can take hold. I’m not proposing to take the directory public.. but at least give regulated entities equal access. In Australia the driver was to decrease bank switching costs, also note that Australia has no Signature debit.. just as in Canada. A common directory could also follow rule that non-regulated institutions could not hold account data (or card number).. Just as I don’t have to know my Bank’s IP address.. I could use another identifier (email, mobile, …) for online transactions. The danger for banks is that this would certainly open up the world of least cost routing to non-banks. Payments would become “dumb pipes”.. which is perhaps what it should be.
Mobile payments is certainly not critical government infrastructure. So what is Government’s proper role? Consumer data protection, transparency, regulatory requirements, equal participation/access.. ? I don’t know the answer. I like the idea of the Government creating a model service for R&D purposes.. perhaps based on Fedwire and letting non-banks have access to it… I also like the idea of a common directory.
ISIS
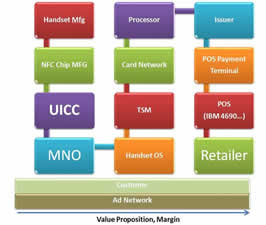
For 2.5 years I’ve been writing about ISIS.. I’ve always have been a huge advocate.. until lately. What has changed? My position, and that of retailers, is that today’s payment networks are heavily tilted in favor of the banks. The opportunity I originally saw for ISIS was constructing a new merchant friendly network that was an “extension” of the current mobile network which the carriers run (The original business case for ISIS is outlined in ISIS: Moving Payments from Rail to Air).
Keeping with my theme of openness and standards how is ISIS creating a platform for other to invest in? What value is an ISIS mobile payment to a retailer? Yesterday’s blog talked about the complex supply chain necessary to deliver on NFC. Don’t get me wrong, there is nothing wrong about NFC technology.. it is a very well defined specification. But it is complex.. if it was a NEW WAY of doing payments (or better yet commerce) perhaps it should have started a little less ambitiously. The team seems as if it prudently sought to reduce risk, but it also gave up on a central element to its value proposition. My analogy for today is that ISIS project is like Vanderbilt’s skipping steam and going straight for high speed mag lev in 1880…. While the entire country was growing at a 10x pace and he had no right of way..
Big projects are tough in normal times.. but mobile is changing at an unbelievably fast pace. Small focused projects are certainly lower risk when innovating at the cutting edge. Everything is changing.. how could anyone architect an open system in such a fast changing environment? It would seem that technical standards like TCP/IP or GSM were successful because of their ubiquity and distributed control. They could be used by all to create different networks with different value propositions.. which incented millions of companies and consumers to invest. I just don’t see how MNOs can create a business platform based on NFC. Their best shot may be to work with someone like Sequent Software to create an architecture for 1000s of applications to access secure element data.. instead of the one single CSAM wallet coming out in Pilot Dec 2012.
Your thoughts are appreciated
Previous Blogs (Nokia NFC Ecosystem, ISIS Ecosystem or Desert, Banks will win in Payments.. but WHICH ones?)