9 January 2011
Previous Posts
It’s the New Year, and thought it was time to touch on this again (last post 9/10). Quite frankly its hard to believe I’ve been writing about this for almost 18 months.. it was AT&T Newco, then Mercury now finally I have a name: ISIS, with a URL www.paywithisis.com (err… same reaction). Over the last 18 months or so I guessed wrong on the consortium around AT&T, it was not Visa, but Discover (See winners/loosers blog above) it was also all of the major US MNOs (Sprint was initially involved, but has delayed further participation). Discover makes complete sense, as stated previously a 3 party network is the only one capable of developing a new payment type (with corresponding set of rules and fees). Visa/MA are constrained by existing agreements with card holders, issuers, acquirers. A principle example is Visa’s failure to force a “mandatory” payment type in Visa Money Transfer (VMT).
Top questions I hear today:
1) What is merchant value now that Durbin has pushed back debit to $0.12
2) Will ISIS work with Mastercard Paypass/Visa Paywave ?
3) Will Phase 1 have a mobile advertising component?
4) What are the economics for a merchant POS “upgrade”
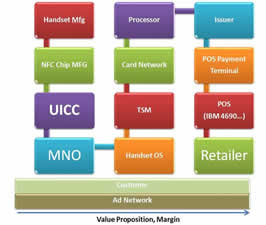
A common basis for many of these questions is the ISIS value proposition, the entities driving it and their incentives. The high level value proposition is shown below, updated from the previous September version (prior to announcement of Barclays and Discover).
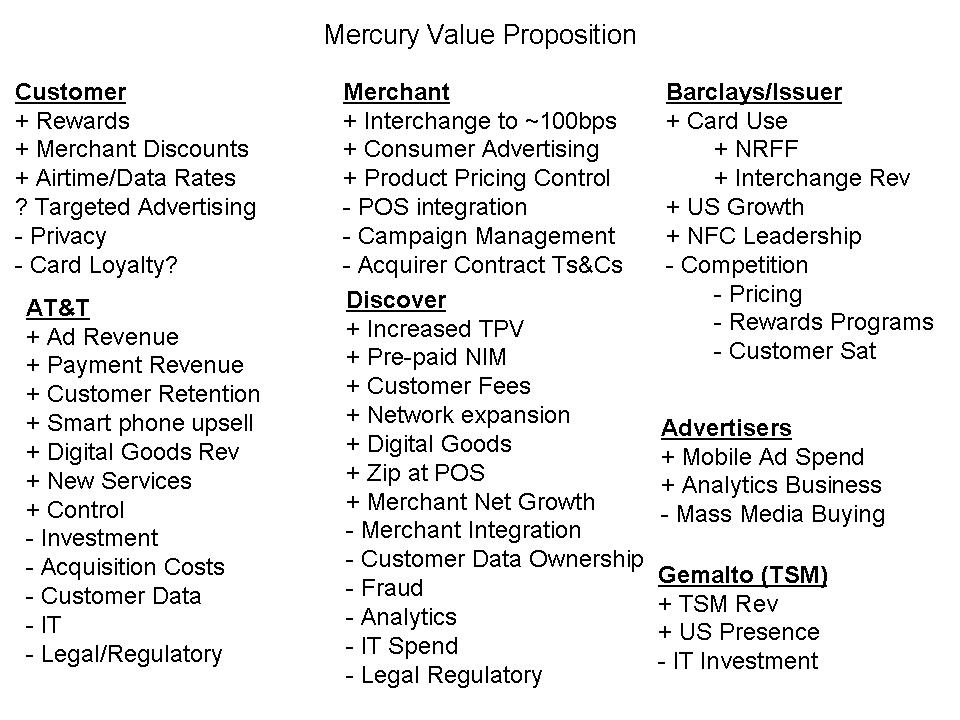
Merchants love the idea of ISIS, as much because of prospective consumer value … as the pain it will bring: Visa, MA and Amex. As one former collegue put it: “Merchants have always loved the idea of instant credit and see value in giving customers the ability to buy regardless of the balance in their account, however merchants don’t buy into paying 1.5% of sales for a debit transactions that was $0.05 with a check”.
Historically, the card schemes have built up much ill will with merchants due to: interchange, payment system integrity, fraud controls, consumer influence, …etc. Two major issuers inferred that Discover is a failed payment “cash back” card network. I would proffer that their “success” is just delayed, and ISIS is the initiative which will drive transaction and network growth in a model that existing schemes can’t compete with. (See American Banker Article). I see a $200B-$600B TPV network evolving with Discover at its core. Perhaps this is why JPM is assessing a Discover acquisition.
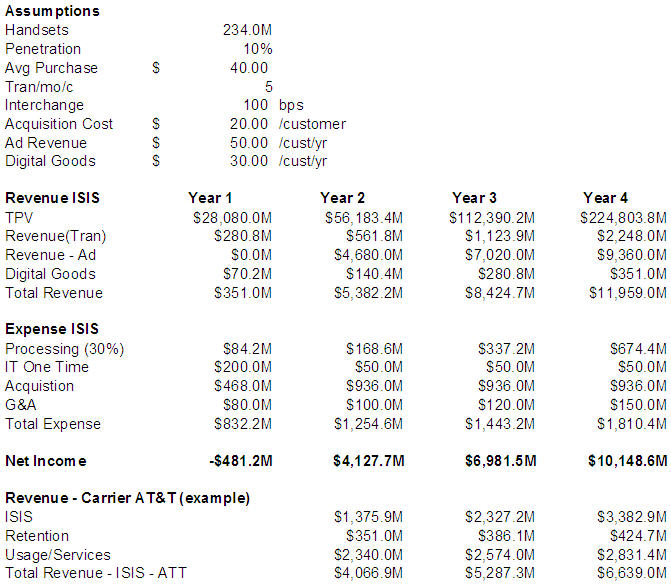
In addition to Discover, I see 5 other entities capable of driving similar value propositions (in the US): PayPal, Amex, Citi+??, Bank of America/First Data, and Chase/Paymenttech.
From an MNO perspective the value proposition is clear (see previous blog). Payments not only supports their existing value proposition to customers, they have the distribution and incentives (airtime, data rates, discounts, advertising) to change customer behavior.
Question 1: Will ISIS take off in light of Durbin and $0.12 debit?
I interpret this as a merchant question. Certainly merchants want the lowest cost payment type used in purchase. What if merchants were “paid” to take the payment instrument? Merchant borne interchange has historically been the major source of revenue for current card products, is there a model where advertising can replace interchange? Googlization of payments?
ISIS has this potential, but will likely not execute against this element for 2-3 years as it develops the payment infrastructure and customer footprint. This may be an issue for ISIS, as merchants may take a “wait and see” approach before investing in POS terminals. This would obviously impact payment volume as merchant NFC POS terminals are just as important to a payment network as millions of NFC enabled phones. If I were Michael Abbott, I would focus on a few very large merchants and commit to a very low interchange (50bps) to drive POS economics that would then support further network expansion. Perhaps this is why we hear so little of ISIS’ merchant value proposition..
So to answer this question, YES it will still take off. I’ve spoke with 2 Fortune 50 retailers this month and they are very firmly committed to making ISIS successful. They see value extending beyond the payment cost itself. That said, there will not be a “big bang” roll out, but rather geographically focused.
Question 2: Will ISIS work with other Visa/MA?
There are many, many sub-questions here. So let’s start with some facts:
1) Discover Zip is different then ISIS NFC (see Story Here).
Geoff Iddison (MA head of mobile) is quoted in NFC times as saying “The challenge that Isis will have is to re-terminalize all of those merchants to a terminal specification which is proprietary”. This is false, ISIS is not using ZIP. They are 2 different initiatives (see ZIP pilot results). The details are best described in this American Banker Article (Jan 2011).
2) NFC and RFID are both based upon ISO 14443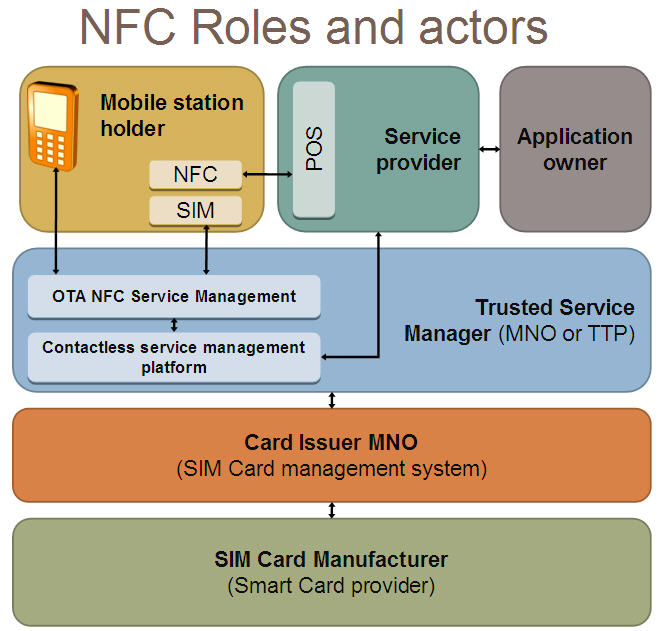
For further info, see the NFC FAQ. And NFC Ecosystem.
3) Merchant POS terminals support multiple standards today
POS terminal decisions have always been independent of card issuers, except where there has been direct subsidies for a “pilot”. Today, POS terminals support multiple staandards (example: VivoPay 8100). Note from a scheme perspective, these POS terminals must be “certified”.
Perhaps this interoperability question should be rephrased to ask if ISIS is constructing any competitive barriers? Does ISIS have unique “standards”? Will ISIS be subsidizing merchant POS terminal? What are the “control” points for ISIS?
The “real” barrier ISIS is constructing is NOT at the POS, but the handset. Specifically, ISIS has created a multi carrier TSM (serviced by Gemalto). For those unfamiliar with NFC ecosystems, the TSM is the entity that owns the “keys” to the secure applications within your handset. Banks want to be in the position to serve in the TSM role, a “DESIRE” best exemplified in FirstData’s TSM brochure:
Card associations believe they are excellent candidates to fulfill the TSM role, and it makes sense from their perspective. The TSM role would make it much easier for the card associations to support their member financial institutions in the issuance of new payment applications and the expansion of the number of accounts they have. In addition, they already have an infrastructure in place for supporting their card accounts.
Banks will not get this TSM role… at least not for NFC which is embedded within the handsets. In the US market, MNOs subsidize phones and already engage in a device “locking” strategy (GSM phones cannot be used with another carrier). US MNOs plan to leverage ISIS and Gemalto (as TSM) to extend this control model to the secure NFC element. In other words controlling which cards and applications can use the device’s NFC capabilities. Note that this dynamic is very “US” focused, as consumers in most other countries buy their handsets unlocked and will have a “choice” of TSM.
This ISIS TSM construct greatly concerns Visa, MA and the large issuers. In the Visa/MA model, NFC transactions are “premium” and can carry very high interchange (see BestBuy Pilot). Merchants are very reluctant to add NFC POS capability if it will increase costs. Although Retailers don’t have to worry about consumers using PayPass or PayWave in mobile phones (due to TSM constraint above), they may have to contend with NFC stickers, MicroSD cards and unlocked phones with NFC capability.
I have no visibility into ISIS, or retailer, plans here. My guess is that the large retailers (which ISIS is working with) will exclude Visa/MA NFC payment types unless there is a an agreement to match interchange. Merchants and ISIS will be emphasizing a new payments brand.. Will merchants allow an Visa PayWave transaction on the same POS? I would imagine that some will, but I would bet that ISIS launch partners will not support PayPass or PayWave. They will tell their customers “sorry … just swipe your card”.
The issuers may contend that agreements in place prohibit discrimination of NFC vs. Card Swipe (retailers beware of this point). I doubt if they will be successful with this argument, given that the merchant is not discriminating but rather accepting a new payment type in a new infrastructure (which the merchant pays for). Durbin, also allows merchants to “steer” customers toward preferred payment types.
Question 3 – Mobile Advertising
I have limited visibility here, but it would seem this is not in scope for Phase 1 of ISIS. Michael Abbott has only been in the job  for a few months, and would expect him to be the driver of plans here given his CMO role at GE Money. One interesting tangent will be what role ISIS allows Apple iPhone to take. It is assumed that the ISIS TSM will still manage the secure element, but Apple will manage marketing. See Apple NFC Patent.
for a few months, and would expect him to be the driver of plans here given his CMO role at GE Money. One interesting tangent will be what role ISIS allows Apple iPhone to take. It is assumed that the ISIS TSM will still manage the secure element, but Apple will manage marketing. See Apple NFC Patent.
Question 4 – POS Economics.
From my perspective, this remains the biggest barrier to adoption (see Federal Reserve Study). Durbin’s reduced debit rates have made a challenging business case even more so. There is a normal refresh rate on POS infrastructure of about 4-6 years. Card networks have typically subsidized POS infrastructure within pilot geographies. It remains to be seen how ISIS will incent merchant participation beyond the marketing value proposition (above).
Summary
Most of you know the story of FedEx Founder Fred Smith, and the college term paper he wrote discussing the market for a next day package delivery service. His professor scoffed at the idea and gave him a “C”. Why would anyone want to ship goods via Air.. and there was no need for a “next day” service. Similarly with ISIS, the banks see no need for a MNO driven payment solution… after all they have all of the technology that ISIS has … and have been doing this for years. The market opportunity for ISIS is in shifting of control away from banks and card networks toward merchants and consumers to deliver a new value proposition that goes beyond payments. The mobile handset has the opportunity to be THE primary device for advertising, content and communication. Payment is only one element, but perhaps the central one as it is enables delivery and tracking of incentives necessary for effective advertising.
Will banks / networks be able to adapt their existing payment rails to the ISIS model? It sure is hard for trains to fly…
Where can banks win? Credit, Risk, Merchant Services, Consumer Preferences, Deposit, Customer Service, … etc.
Thought appreciated