17 Feb 2011
Digital goods are everything that can be sold and shipped online (music, movies, articles, ring tones). John Doerr (legendary KPCB Partner) certainly turned heads in Nov 2010 when he said Zynga is “our best company ever”. What is driving the explosive growth in digital goods? Social gaming. The nice thing about running a credit card network is that you can see who is making money. No doubt a factor in last week’s $190M Visa acquisition of Playspan.
A key benchmark in the category of “digital goods” is Apple. Within Apple’s annual 10k digital goods revenue is accounted for within the “Other Music Related Products and Services” category. This category also includes app stores. For FY10 Apple saw a 93% increase in iPhone sales, but there was only a 23% uptick in “digital goods” (growth in line with previous 2 years). This makes intuitive sense given that Apple customers did not need to repurchase their iTunes library from iPod 1 to iPhone 4. But Digital Goods has certainly NOT been a key source of growth for Apple.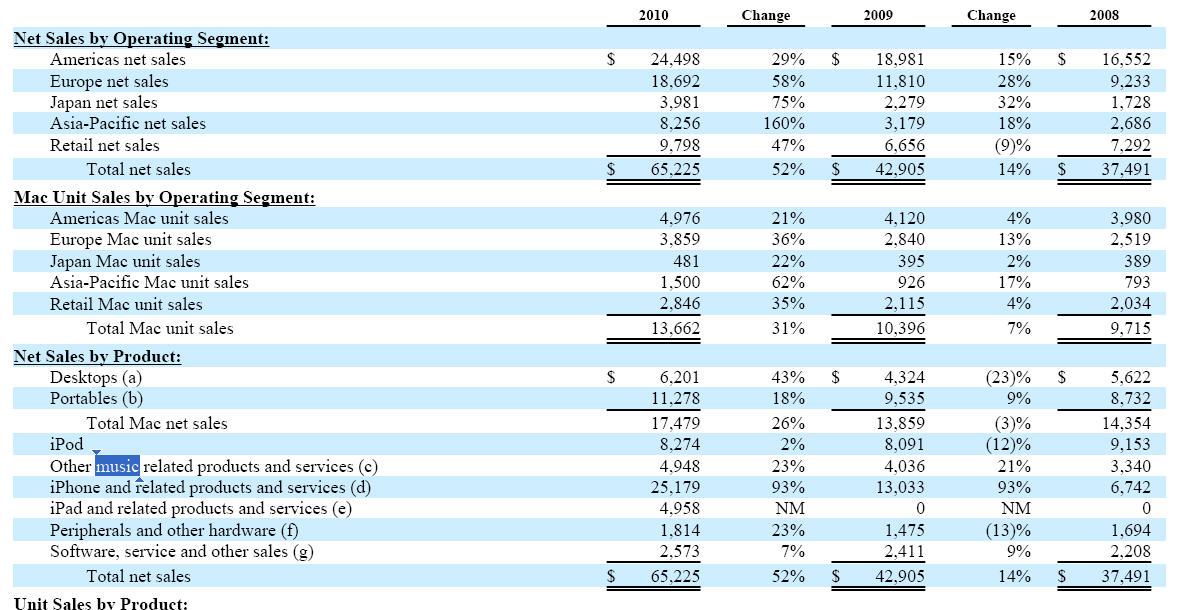
Lets take a look at Zynga. As I stated in previous blog,
…three years old with an estimated market value above $5 billion with more than 320 million registered users and estimated revenues above $500 million… From my perspective, Zynga’s secret sauce has been its ability to get 1-2% of their customer base to pay for game credits (see Gawker article). Although they have recently agreed to a 5 year deal with Facebook, this patent (if granted) will provide them leverage in future negotiations and extending their services outside of the Facebook platform.
For more info see TechCrunch / Steven Carpenter Zynga analysis (excellent)
The fortunes of Zynga have been tightly tied to the success of Facebook. Facebook’s new payment policy (mandating use of Facebook credits) will enable them to capture 30% of revenue. Zynga’s margins are obviously impacted in this move.. I’m sure many people immediately see the analogies here with today’s WSJ article (Apple Risks App-lash…) on Apple’s 30% digital goods tariff.
As an investor, where do you place your social gaming bets?
A foundational digital goods investment question is your view on how social gaming can exist. Can social gaming survive in a model disconnected from Facebook and Apple? If you believe so, then possibly place bets in the Google model. Over the past 6 months, Google has made five acquisitions in the field: SocialDeck, a mobile social gaming company; Angstro, a social networking search application; Like.com, a social fashion store; Jambool, a social gaming virtual currency; and Slide, a social game maker, and a $100M+ stealth investment in gaming giant Zynga. Beyond Google, other views exist for social gaming in a mobile context (MNO driven model).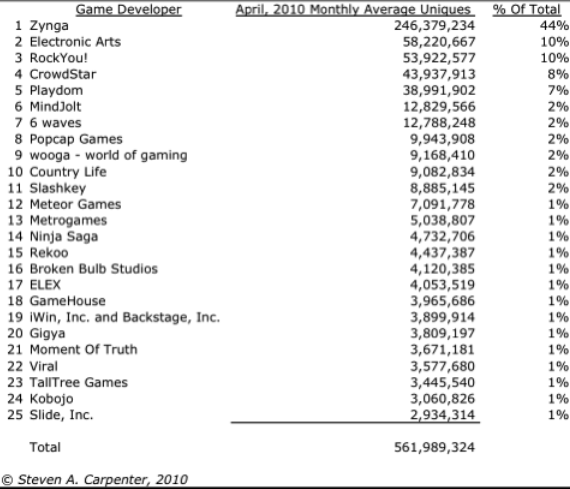
Now that you have chosen the model (I’m tired of using the word ecosystem), where will your bet play? I see 5 categories:
- Games (Zynga, EA, …)
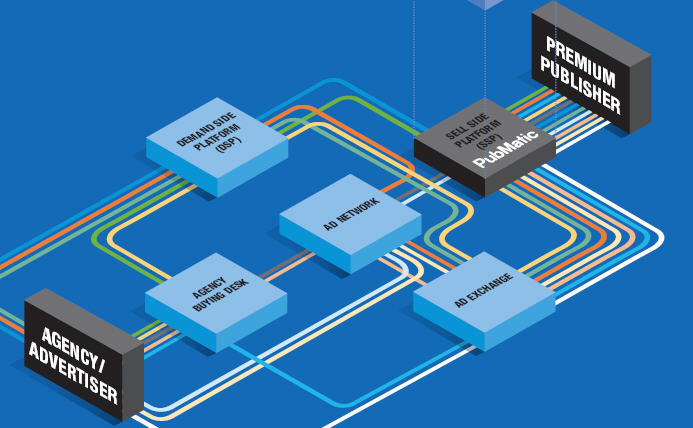
- Analytics/Incentives/Advertising
- Distribution
- Gaming Infrastructure. Example Payment, Hosting, Mobility, Support, …
- Confluence. game-community, game-retail, game-mobile, game-mobile operator, … Example.. earn farm $$ by visiting a retail store and checking in..
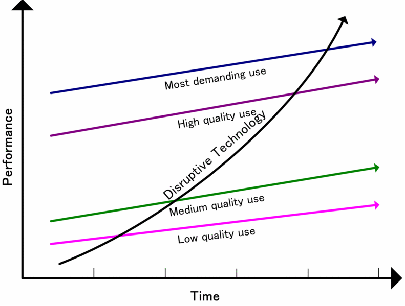
Is social gaming a sustainable category? My personal preference is to place bets in common infrastructure until the next Zynga flourishes. Something I learned from Larry Ellison “when there is an arms race, don’t fight.. sell the guns”
Feedback appreciated..