Tag Archives: JPM
Private Label.. “New” Competitive Environment?
JPM/V Scenarios… Which one is it?
MNOs giving away Billions to Banks.
Future of Retail Banking: Prepaid?
Nov 7 2012 (updated for typos)
Warning.. long monotonous blog. Sorry for the lack of connectedness, written over 7 days and my editor is rather slammed. You have been warned, so don’t complain….
Summary
- The competitive dynamics surrounding a “transaction account” (ie DDA) are shifting. For example, Retailer banking/prepaid products (Wal-Mart, Tesco, ..) offer significant fee advantages to most lower mass customers. Three party networks like Amex and Discover have unique advantages when combined with Retailers distribution/service capabilities. This means prepaid has become a disruption: a new good enough product…
- Net interest income is 64% of total US retail bank revenues, yet the bottom four deciles of mass market customers are no longer profitable. Given that the transactional account is the #1 factor for retail bank profitability, what are implications if banks loose it?
- There is a high probability for disruptive value propositions in Payments, as advertising replaces merchant borne interchange. Payments and core banking will become a “dumb pipe” business unless Banks create value and assume a larger orchestration role. POS Payments are the central feature of a transaction account, if banks loose this relationship they will be in a poor position to orchestrate.
Does anyone else have trouble keeping up with state of the art? Who is doing what? My method of keeping up with change is to immerse myself in a given area for a day or two. It also gives me a reason to call my friends and colleagues. This week the theme is retail banking. I’ve spent too much time thinking about payments and how it relates to mobile, advertising, …etc. I thought I would dust off my banking hat and think in terms of a banker.
Retail Banking
I’m struck by how odd retail banking is. Why are banking services not more simple? Why do I have a separate savings, checking and card account? Why not one account? if the account runs in a arrears I pay interest and if it runs in credit the bank pays me interest? Why does a bank take 3-5 days to move money? How on earth do the banks afford all of those stand alone branches when I visit them perhaps once or twice a year? Why all of the regulation? What does my bank do for me? What problems do retail banks solve? Can someone else solve these problems more efficiently?
There is certainly no single answer. Retail banking serves many demographics, from the college student to the billionaire. Historically retail bank relationships were very important relationships, as banks only lent money to people they “knew”, based on the deposits they had. Younger consumers need to borrow, older consumers … savings. Banks focused on things like college student accounts to lock in that relationship as early as possible. Today’s modern financial markets provide for the securitization of loans, thereby spreading risk among various investors willing to assume it. Does a banking relationship matter anymore? to Consumers? to Banks?
I’m struck by how little change has occurred (in the US) on the liabilities side of the banking business? Quite frankly US consumers are treated like idiots who sacrifice “protection of capital” over risk. We now have an entire agency working to protect US consumers 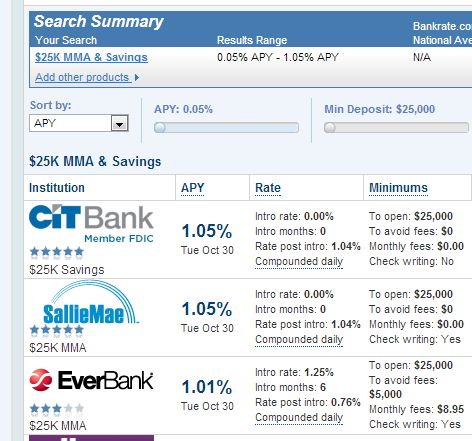 from banks.. (BTW what is predatory lending?). Other markets let consumers take on risk.. and hence have many more choices, and innovation, in savings. For example, I’m very fortunate to have worked with so many fantastic people over the years. The great thing about running Citi’s channels globally is that each and every country had a somewhat unique competitive and regulatory environment. It was like running 27 different banks. There were many different strategies for deposit acquisition, for example:
from banks.. (BTW what is predatory lending?). Other markets let consumers take on risk.. and hence have many more choices, and innovation, in savings. For example, I’m very fortunate to have worked with so many fantastic people over the years. The great thing about running Citi’s channels globally is that each and every country had a somewhat unique competitive and regulatory environment. It was like running 27 different banks. There were many different strategies for deposit acquisition, for example:
- In Spain we had a 10/2 product that paid 10% interest on deposits for the first 2 months.. then went to 1%.
- In Japan Citi leveraged its global footprint, and the poor local consumer rate environment, to create foreign currency (FCY) accounts which allowed consumers earn higher returns by assuming currency conversion (FX) risk in uninsured accounts.
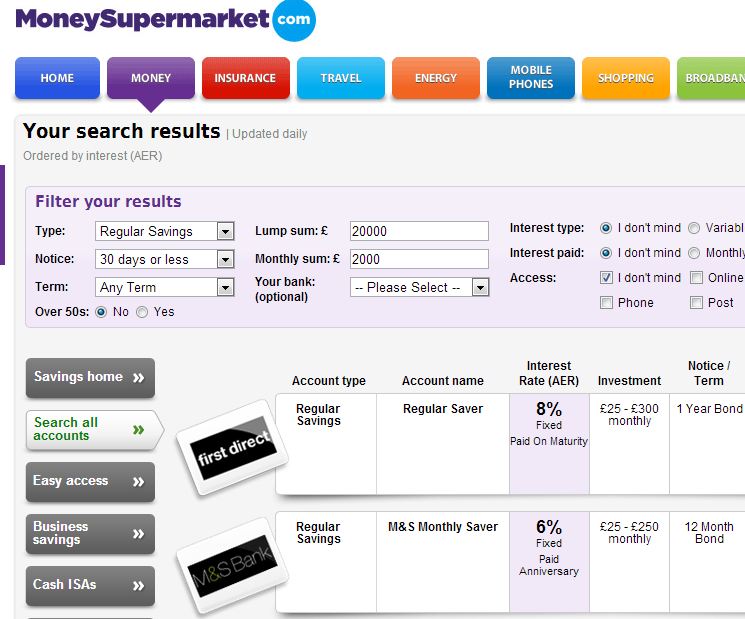
- The UK is perhaps the most competitive retail bank environment in the world. Consumers in the UK can switch banks almost as easily as changing shoes, it was thus essential to enable consumers to switch quickly and then get them into other products quickly. Take a look at today’s UK savings rates from MoneySuperMarket (8% on a fixed $30k deposit) vs the US (1.05% bankrate.com). Rate differences on this scale helped fuel the carry trade in Japan.
In the US, it is well known (inside the banking community) that banks are highly discouraged from competing on rates. Not that it matters, this amazing study by the Chicago Fed (Chicago Fed – Checking Accounts What Do Consumers Value – 2010) shows that US consumers are rate inelastic.. and care much more about fees. You have read this right, consumers don’t care about interest rates on their deposits.. which is certainly NOT intuitive. Perhaps rates are all so close to 0% that 5-10bps doesn’t matter. Or perhaps because the average US consumer does not save at all, and those that do have their money in another place.
Retail Bank Profitability. Net interest income (2011, represented more than 64% of total US bank revenues) is the rate spread between borrowing short and lending long, or more broadly the differential between asset yields and funding costs. Net interest  margins (defined as net interest income over average earning assets) were 3.6% at year-end 2011, just 11% higher from the 20-year low of 3.2% in the last quarter of 2006.
margins (defined as net interest income over average earning assets) were 3.6% at year-end 2011, just 11% higher from the 20-year low of 3.2% in the last quarter of 2006.
From DB Research
As low rates persist, loan-to-deposit spreads fall as prices adjust, and longer-term securities, held as assets, roll over to lower-yielding securities (the same holds true on the funding side, of course, helping to extend the positive impact of falling interest rates into the future). The net impact on banks’ net interest levels may be negative, though. In previous recoveries, this effect has been offset by increased loan volumes, allowing banks to return to sustainable growth levels. Furthermore, as an economy recovers, banks may quickly benefit as short-term assets roll over at higher rates
To summarize: Bank net interest income is important (64%), and falling. Banks have had a key revenue source taken away from them (Debit interchange) and are also facing another merchant led suit on credit card interchange. Bank brands and reputations are on a steady downward trend. Consumers don’t care about rates, but react strongly on fees. … A new regulatory agency to protect consumers is just now forming and looking to make its mark. What are banks to do?
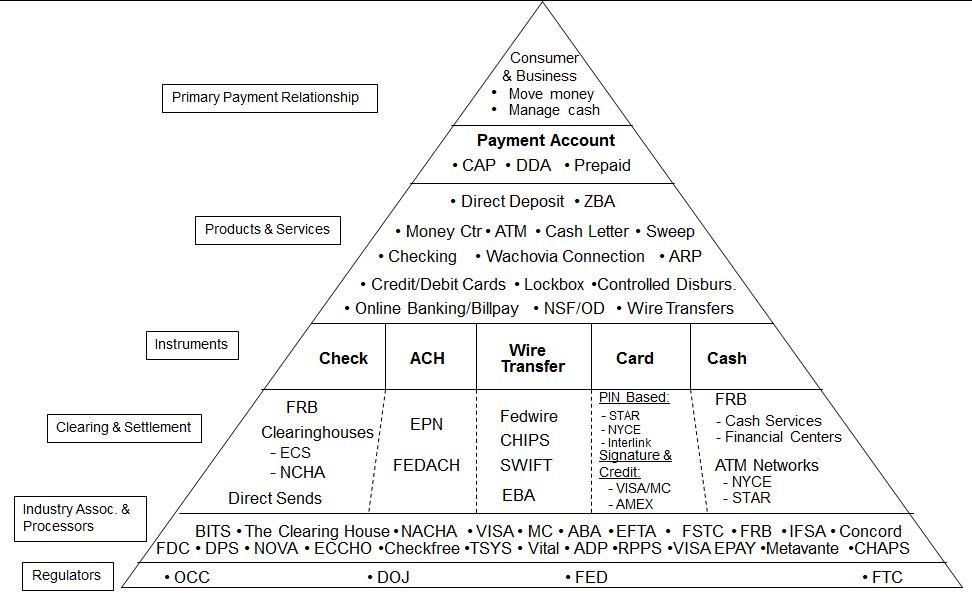
Transaction Account
What is the purpose of a bank provided transactional account today? Well certainly our mattresses are a little less lumpy, and the relationship factors have largely gone away. So what is left? Transactionality?
The banks have long recognized that the transactional account is the #1 factor driving a consumer relationship. Virtually every other banking product and service hangs from this account. Most retail banks view direct deposit (internationally known as Salary Domiciliation or Sal Dom) as the key indicator of the transactional relationship. Consumers have limited “energy” to connect to more than one network (as outlined in followed my previous blog on Weak Links).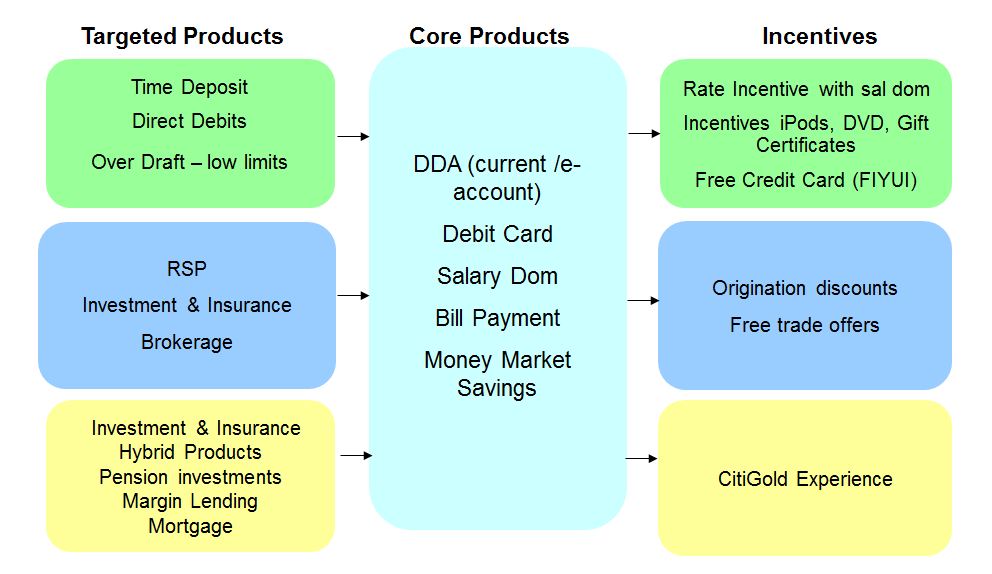
This financial supermarket concept, authored by Sandy Weill and John Reed, has not exactly been a slam dunk success. Nonetheless every retail bank starts selling with a checking account, even if nothing else is attached. What are the key factors influencing the selection of a transactional account?
- Why are deposits important to banks?
- Driver of overall relationship à Customer Net Revenue
- Liquidity ratio ->Risk ->Agency Rating -> Capital Costs
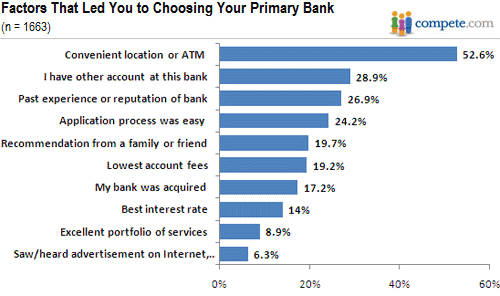
- How do consumers select a bank?
The public compete data above is completely consistent with previous proprietary studies I’ve commissioned. Consumers tend to pick their bank based on how convenient the branch and/or ATM is.
Is there something fundamentally changing? What if consumers don’t visit a branch… or no longer use cash? Are there new value propositions? Where will consumers (and their deposits) go?
Recent market developments/Announcements
- American Express/WalMart BlueBird
- Tesco Bank
- Merchant Consumer Exchange (MCX)
- Safeway activating ACH on Club Card (Fast Forward)
- American Bankers Association – Prepaid from Banks
- Network Branded Prepaid Card Association (analysis)
- Barclays Pingit Service
- Google Wallet goes Plastic
- MNOs rule in Emerging Markets
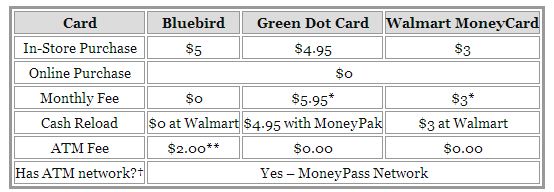
The Amex Bluebird product is revolutionary in terms of fees. It is the lowest cost reloadable card in the market today. Beyond the product, I’m even more impressed with WalMart’s business strategy here. They seem to be willing to break even on payments/banking in order to win the overall consumer relationship and increase foot traffic and loyalty in their stores. Take a look at the suite of products offered by WalMart. While banks are pushing out the bottom forty percent of mass consumers, WalMart has made a bet that it cannot only serve them, but do so profitably.
There are many different types of pre-paid cards (more below), however most are not regulated as bank accounts. In almost every geography, consumer deposits (interest bearing, insured) are regulated because they drive both bank liquidity (which drives lending and cost of capital) and profitability. Remember before capital markets existed to securitize assets (loans) retail banks could only lend to the extent of their balance sheet (deposits). Consumers put their money with banks in order to earn interest (the carrot) with the downside of fees on usage (the stick). In the US consumers are beginning to ask themselves “is the carrot big enough”?
In emerging markets many banks have a poor reputation, additionally access to legal resources are limited, as are consumer protections. How would you feel if you showed up to your bank for a withdrawal and your bank said “sorry your money is gone” and you had no recourse? This dynamic has propelled other banking models in emerging markets. For example my friend Nick Hughes and his Vodafone/Safaricom team created MPESA in Kenya which provided enormous value to consumers. However MPESA caused an apoplectic reaction from the banking regulators as 10% of Kenya’s GDP sat in a non-interest bearing Vodafone owned settlement account. MPESA therefore impacted bank liquidity (IF the funds would have gone into a bank account as opposed to just M1/cash). Visa and MA have worked hard to try to make prepaid the underlying account for mobile money in emerging markets, to very little avail. The problem is not connecting people to the V/MA network.. and giving balances to an approved bank. The problem is first transferring money to entities currently not on any network, then paying a very small number of billers. 
Why are consumers defecting in the US? Ernst and Young just published a phenomenal global study on this subject. The result of their analysis was that consumer confidence in banks is degrading. E&Y outlined a call to action by banks: reconfigure your business models around customer needs. My hypothesis is that consumers have reached a tipping point where they view banking services as commodities… In the UK, this is already well established.
Prepaid
I haven’t spent much time thinking about prepaid cards so I thought it was time to refresh myself, particularly in light of MCX and the prospect of retailers acting as Banks.
From the US Fed
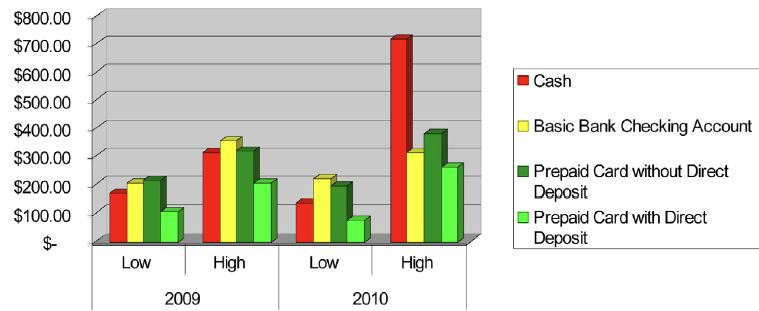
Prepaid cards offer much of the functionality of checking accounts, but that does not mean the underlying economics are the same. A typical prepaid card in the data is active for six months or less, a small fraction of the longevity seen with consumer checking accounts. As a result, account acquisition strategy and the recovery of fixed and variable costs are likely different than for checking accounts. …. prepaid cards with [direct deposit are uncommon but] remain active more than twice as long and have 10 times or more purchase and other activity than other cards in the same program category. As a result, these cards typically generate at least four times more revenue for the prepaid card issuer
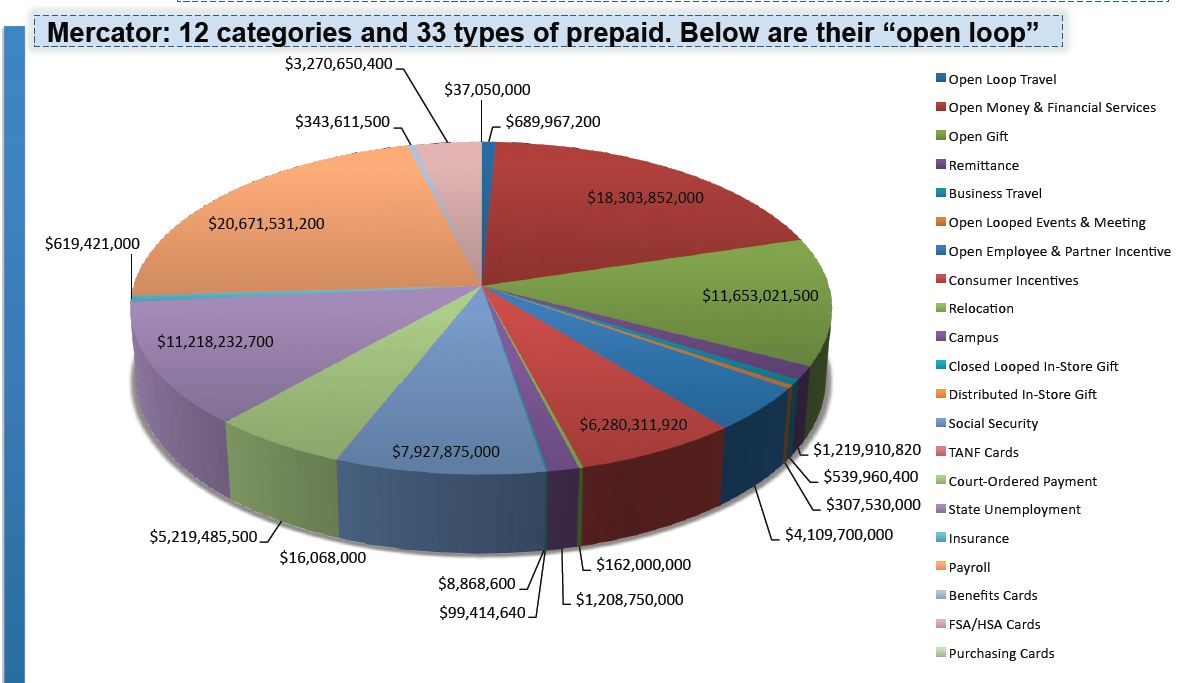
Similarly Pre-paid cards also face a complex web of regulation (See Philadelphia Fed Paper 2010), across 31 different types of cards.
31 types of cards? Did anyone else realize the diversity here? Wow… For the sake of this blog, let’s focus on reloadable (GPR) open loop cards (references to prepaid below are on this card type only). It would seem that GPR pre-paid is following the general disruption pattern of serving a lower tier of the market at a more attractive price point. According to Mercator, In 2009, consumers loaded $28.6 billion onto prepaid cards. By 2015, prepaids will hold $168 billion.
Last month’s WSJ ( Prepaid Enters Mainstream) outlined this dynamic
Traditional leaders in GPR pre-paid have been Green Dot, NetSpend, . The Durbin amendment exempted most prepaid cards. This means that pre-paid is largely example from the Durbin interchange restrictions… (with several conditions). Thus the business case for pre-paid is rather strong, and Banks themselves are assessing if they can make this the new “starter” account (ex Chase Liquid). However Three Party Networks (Discover and Amex) have a significant advantage.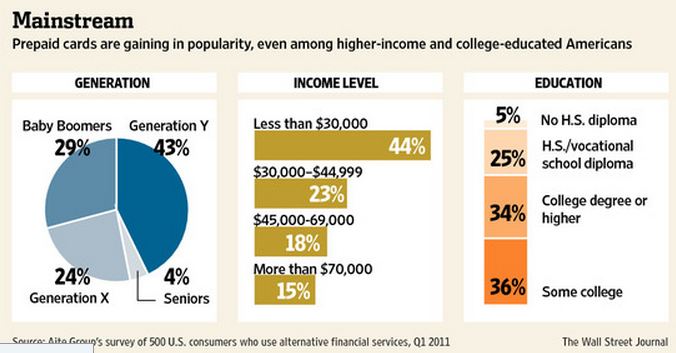
From Digital Transactions, March 2012
While the Federal Reserve’s rule implementing the Durbin Amendment has its greatest effect on traditional debit cards, it affects prepaid cards too, especially its provision that banks’ prepaid cards can avoid Durbin price controls only if cardholders can access the funds exclusively through the card itself. That provision thwarted banks’ efforts to make prepaid cards more like demand-deposit accounts and led them to scale back or end bill payments through prepaid card accounts.
But American Express and Discover are not subject to Durbin’s controversial provisions, Daniel and Brown noted. Both companies are so-called “three-party” payment systems that function both as merchant acquirer and card issuer. In contrast, Visa and MasterCard debit and prepaid cards are part of “four-party” systems in which the issuer and acquirer are usually different companies and rely on the Visa and MasterCard networks to route transactions among them. The Durbin Amendment exempts, or “carves out” in industry parlance, three-party networks from its provisions, including interchange regulation.
“There’s no restriction on what AmEx can pay itself” for prepaid card transactions, said Brown. Thus, AmEx and Discover have a new opportunity to grow their prepaid businesses, the attorneys said.
Clearly Discover (DFS) and American Express (Amex) have an opportunity to “Kill” prepaid cards, what are they missing? Physical distribution, service and reach in the mass market. These are the very things that retailers like WalMart can provide, and in fact economically benefit by providing them.
As you can tell, regulations are driving the business models here. Most large US retailers leverage a fantastic team of attorneys from Card Compliant that specialize exclusively in prepaid cards (run by my friend Chuck Rouse). WalMart’s move to Amex is brilliant both from a regulatory and business model perspective. 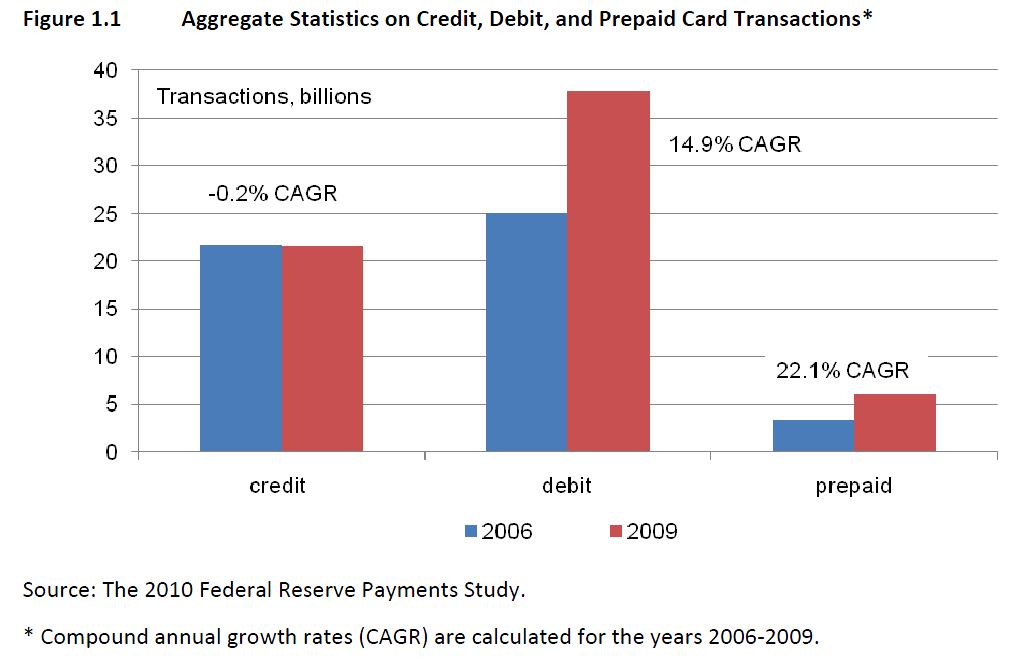
Today’s pre-paid dynamics may be the tipping point by which 3 party networks begin to overtake V/MA in growth. A trend that will accelerate when other business models require “control”. This next phase will be centered around merchant/consumer transaction data, which will begin to unlock the advertising revenue pool, which is almost 4 times larger than that of payments.
Payments and core banking will become a “dumb pipe” business unless Banks create value and assume a larger orchestration role. POS Payments are the central feature of a transaction account, if banks loose this relationship they will be in a poor position to orchestrate. 4 party networks are very, very hard to change.
I see a battle where 3 party networks work to branch into orchestration and advertising, and existing orchestrators (ie Apple/Google) integrate legacy dumb pipes (payments and telecommunication) to deliver value to the consumer. What do consumers value today? This is the call to action for bankers… who are not always the best at creating alliances.
Here is one idea, focus on trust and helping consumers solve problems they don’t face frequently. For example,
- Make financial planning easier and less of a sales job.
- Help manufactures and retailers connect to target consumers.
- Become a buyers agent?
- Help navigate the college application and loan process,
- Help buy a new car for the lowest possible price…
I know this is not a clean finish.. but that’s all the time I have.
References
- August 2012 US Federal Reserve – Consumer use of prepaid cards
- Federal Regulation of the Prepaid Card Industry – April 2010
- Chicago Fed – Checking Accounts What Do Consumers Value – 2010
- AT Kearny Retail Banking Profitability – Europe
- Network Branded Prepaid Cards Association (NBPCA)
- American Banker – Amex Prepaid Card
- Center for Financial Services Innovation
- Top Global Brands – Interbrand
- WSJ Prepaid Enters Mainstream
Thank you Kansas City Fed for the fabulous brief from the: CONSUMER PAYMENT INNOVATION IN THE CONNECTED AGE. Bill Keeton and Terri Bradford were nice enough to invite me, but unfortunately I couldn’t attend. In my last visit to the KC fed we spoke about future payments types, but we also spent quite a bit of time discussing where mass market consumers will go if banks view the bottom 4 deciles of retail banking as unprofitable (according to proprietary McKinsey Study). Today I thought I would pull together a compendium of my learnings on retail deposits, MSBs and pre-paid… the “transaction account” by which payments flow.
Debit Fees – Newton’s third law in banking
2016 – This post is 4+ years old now.. I wouldn’t take it too seriously.. but good historical context
1 October 2011
First… 2 paragraphs of venting and perspective.
I was quite surprised to see BAC’s $5/mo debit card fee on the national news today. Personally, I think it is a great thing.. customers should pay for services they want to use.. sticking the merchant with the cost of debit leads to some very poor incentives. One of the biggest “innovation stifling” problems we have in the US is that consumers don’t care about prices, for things they should (payments, health care, fraud, education, … ). The cause? the direct costs are hidden. Once consumers bear direct costs for services, market forces can take hold.
This is not to say I’m a supporter for HOW the Durbin change came about.. Dodd-Frank, Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act represent the most sweeping changes to financial regulations in the United States since the Great Depression. From my perspective the timing could not have been worse. Did Congress think the banks would just sit on the sidelines and patiently suffer? After being forced by regulators to act in good faith and “acquire” ailing community members like Country Wide? To suffer again as State AGs and the CPFB go after them for a few billion more (robo-signing). Retail banking is becoming a very unattractive business, particularly in the lower mass market segments. For the recovery to take hold, we need banks to be healthy… these are not a bunch of “fat cat” millionaires.. but a core component of commerce that is instrumental in managing the lifeblood of our economy.
Debit Reaction.. equal and opposite
Well the banks have reacted to the finalization of Durbin fees. As I related in my previous blog on Debt, the fee plans have been in the works for some time, and for good reason: the lower mass segments are no longer profitable. US banks are well capitalized…. with excess liquidity, and a cost of funds near zero. There is very little incentive for them to seek to increase their deposit base (improve liquidity ratio). The core issue in retail banking profitability is asset quality (few qualified people to lend to… who want a loan). This is even more true now that Dodd-Frank has virtually gutted retail banking fees. Two excellent articles below detail the role of transaction revenue and service fees in retail banking.
http://www.bai.org/bankingstrategies/payments/general/protecting-dda-profitability
http://www.novantas.com/article.php?id=317
http://www.standardandpoors.com/ratings/articles/en/us/?assetID=1245235038776
Of course not all consumers will be paying this $5/mo cost. For example, the folks reading this blog will likely have account relationships that warrant a fee exception. Mass market customers will likely be up in arms and seek to move their accounts.. believe it or not.. this is what the large banks want to happen since many of the lower tier customer segments are no longer profitable.
See this American Banker Article for more detail on alternatives to mass market customers
In the next phase of bank plans, expect the Visa logo to disappear from the standard card issued for a base checking account. The card will operate as ATM card, just as it did 20 years ago. As a side note, the banks (and PIN Debit networks such as Star, Pulse, NYCE) will be working with merchants and processors to expand adoption of PIN Debit separate from the card networks.
Market Forces in Payment
Now that consumers have to bear the costs of using a Debit Card. They have new choices:
1) Use credit card. This would be best for the banks, and perhaps best for the consumer as they collect merchant funded card reward points. The looser here is obviously the merchant. An important point to make here is that this is exactly the strategy behind new NFC based mobile payment types.. there are NO NFC enabled debit cards.. banks and the networks want you using your phone for payment to drive credit card usage. This is also the strategy behind Visa’s new EMV mandate, to drive retailer reterminalization. This will be a subject of a future blog.
2) Leave the bank and use pre-paid cards. This will certainly be the path for many lower mass customers
3) Pay the fee
4) Improve your relationship with the bank to meet a threshold and avoid the $60/yr fee.
5) Shift your transactional relationship to new “non bank” structures like PayPal or Google Wallet (both of which are licensed MSBs in all 47 states).
Downside for banks
CEOs make decisions based on data they have. The first 4 options have all been through. I would profer that creating a market for new competitors has not. I outlined in my previous blog “Banks will WIN in payments.. but WHICH ones” that banks are firmly in the position of control today. However there is a strong correlation between control and value delivered. In my upcoming blog I’ll describe how to value a payment network. My view is that payments are on a course of a utility service (i.e. dumb pipes with least cost routing), and that payment services are only the last step of a much more important commerce interaction. Any network business is highly dependent on balancing a value proposition between participants. Today retailers and consumers are not pleased. I only wish I could tell of you the wonderful things I’m seeing in Silicon Valley… IT IS NOT about technology.. but about creating business value.
Within 5 years, I see the strong possibility that a new network which will be able to PAY merchants for accepting a payment method.. (see my 2009 Blog on Googlization of Payments).
BTW… sorry for the lack of content this last month.. I have 15 page blog I’m about to publish.. I will never again try to write so much in one article.
Clearxchange – Bank Strategy Perspective
28 May 2011
As I related in last week’s Post, Clearxchange (let’s call it CX) evolved out of the online/mobile payment groups at Wells and BAC. I also described how bank’s will “Win in Payments” along with a high level view on internal bank dynamics which drive Debit/ACH vs. Credit payments strategy, as well as the fragmentation that is occurring in “unprofitable” payments like ACH, carrier billing and P2P… etc.
Consortiums are not the most nimble of creatures. Banks also have the tendency to follow the lead of the big 3 (BAC, WFC, JPM) in all things retail. BAC/WFC are well positioned to execute in CX, and certainly have a sufficient customer base to make CX work. Their addition of JPM (and associated QuickPay) and the creation of a separate entity also aligns well with getting something done quickly. Developing CX within an existing bank consortitum could have taken much longer than 2 years to get a common bank service built… This “build it and they will come” approach is how many of today’s bank services get their start (visa, interlink/debit/ , clearing house, …).
Unfortunately, CX does not have a sustainable “stand alone” business case. Because it was completed within the channel organizations, business strategy (with the LOBs) was not well coordinated with the other LOBs (exception is JPM, the top bank in payments strategy). I’ve actually made 5 CX payments on launch day already. In BAC, just go to internal transfers and fill out the form on the left (did you receive a transfer). I clicked yes as it did not require an accurate answer in the Ts&Cs..
The service is very solid, but I do wonder what the retail wires group must think. Most bank services today allow for transfers to and from accounts I own at other FSIs (we call this A2A). Now I can transfer money to anyone via mobile with no fee (p2p). What about P2B and impact on Debit? For example, eBay purchase? Or how about at a store? If I can send money to a person with no fee.. what prevents cannibalization of Debit? Because of Durbin making Debit “almost free” is there an incentive to create a new payment network?
My sources tell me that there has been very little planning around CX (outside of JPM) to answer these questions. Not only were people with the big 3 banks scrambling to explain the service internally, their CEOs were getting called by peer banks about why their bank had not been asked to join? While banks are not free from anti-trust concerns.. payments is a network business that requires broad participation. The CX announcement comes at a rather sensitive time for them, as Jamie Dimon chairs The Clearing House meetings, there is little doubt that TCH has also served a forum for coordination on all retail payment “industry matters” like Durbin. Can you imagine working with JPM, BAC and WFC in TCH meeting on retail debit strategy.. then hearing they have a new service rolled out without your knowledge? Not the most polite thing to do.
It certainly was not Jamie’s fault (my favorite bank CEO by far.. fellow Citi alum).. but rather the poor “payments” coordination within banks. In my previous blog Bank’s Need Payment Councils, I laid out how these bank teams had worked historically. CX is a fantastic idea.. and it could even evolve into a profitable service if banks can improve the way the coordinate internally. This is a CEO level decision.. no one wants to tell the CEO that he needs to create a cross LOB council to coordinate payment strategy.. The Citi approach is much more “get a guy to own it”.. like Wayne at Citi, Vin at Chase, or Steve at WFC. But decisions that impact multiple LOBs are very challenging to coordinate across the organization.. CX is the manifestation of just such a dynamic (better to get something done.. then work in a bank committee that never makes a decision).
I’ve been getting called this week on “what is the CX strategy”? The answer depends on who you talk to. BAC has a number of debit/retail payment initiatives.. and there are certainly overlaps..
– New Visa Debit with BAMS/First Data
– Visa Money Transfers (directly competes with CX)
– CX
– Internal Payment Warehouse (3 yrs in making)
– Cashedge (A2A money transfers)
– Pariter (On we w/ WFC)
– NFC Credit w/ Visa and Device Fidelity
– …
If banks have trouble coordinating internally.. the situation certainly does not improv
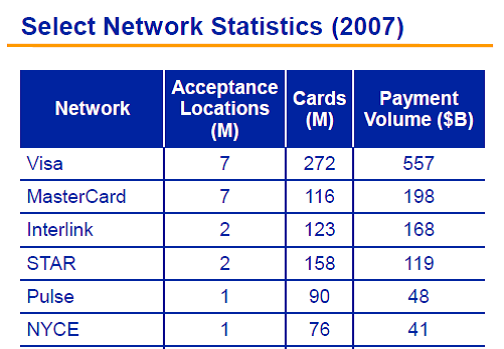
e when 20+ of them get together to set a strategy. Of course this “least common denominator” is why today’s existing payment network is both rigid and resilient. What the banks really need is a firm “platform” vision for payments that they own. For example, what if I broke payments into 3 broad categories: pay before, pay now, pay later? Having multiple products that compete in these categories is a sign of a good healthy market.. having multiple networks process the payment is NOT (only some of which are bank owned). As a side note, there is little reason to doubt that there will be SUBSTANTIAL consolidation surrounding the 6 major debit networks (Visa, Pulse, Star, NYCE…)
My top idea for CX to drive a little incremental revenue? 2 years ago, Metavante (now FIS) negotiated a PayPal deal that would provide for revenue sharing for eBay merchant payment.. PayPal collects 3%+fees and would share 30-50% with FIS. Why would the banks not want to do this? The original plan had more to do with this happening over bill pay.. but a transfer probably makes more sense. Either way, the banks should jump on this kind of opportunity. My #2 idea.. well I’m only telling my customer this one.. (my poor attempt at a tickler).
Happy Memorial Day
– Tom
Clearxchange
25 May (updated)
Banks take back mobile momentum!! Everyone else.. stay away from P2P because this team will own it.
BAC, JPM and WFC launch Clearxchange .. a mobile pay anyone service. This is a very solid idea by the 3 top US retail banks… after all why should PayPal route funds between banks? Banks have always had the capacity to make this work, but have lacked the structure (and business case) to pull this together. Their real risk was banks loosing the “directory battle” (referred to in my previous blog on Chase QuickPay). The last Bank driven initiative of this scale was Spectrum in 1999 where banks decided that acting together in electronic bill payment was the right thing to do..
A short history on this initiative. WFC and BAC got together and created Pariter Solutions a few years ago for “on we” clearing of ACH and images. Pariter initially received the charter to also move toward developing “on we” clearing for mobile/online P2P transactions, but this was pulled late last year as Pariter was having challenges executing against its core mission. Subsequently BAC and WFC got together and created Clearxchange to develop a common “directory” and online/mobile application infrastructure for P2P routing (ACH processing is TBD, but likely to be handled by host organization with clearxchange as a 3rd party sender).
Chase was an early leader here.. QuickPay delivers all of the functionality of Clearxchange… plus some. At one level, I view clearxchange as building what Chase (and Cashedge) already have. Chase has agreed to participate in directory sharing, so that Chase customers can send/receive to Clearxchange customers.
I’m a very big supporter of ClearxChange’s bank led P2P model, banks must own this for this service to take off. Remember, retail payments are a money looser for banks, the WSJ article did an excellent job describing the dynamics. By taking the lead, I would hope other banks also participate directly with ClearXchange or through Cashedge’s PoPMoney service (described here in blog).
Moving money via ACH is technically simple, the real challenge is in risk/fraud management. On this level, there are only 2 organizations with substantial fraud management skills in cross bank P2P: Cashedge and PayPal. Both have 10+ years of ACH history. In the last few years banks have collaborated in developing shared fraud models (can’t really discuss specifics for obvious reasons) that now allow them to substantially reduce risk without prior transaction history. The long term objectives of CX are rather vague (bank control of ACH rails, and balance retention in DDA). Their short term plan is to move consumers to a “push” model, where funds are sent from a bank authenticated log in. Banks want to be the starting point of a transfer. This positions them as the trusted intermediary, with benefits in fraud and cementing consumer behavior. This is a significant announcement with over 3 years of planning behind it.. but scope is narrow.
The push (ACH Credit) P2P model, where customer initiates transfer from their bank, has a poor history (search on “Paybox success”). The historical issues here have nothing to do with technology, but rather business model: simple and free funds transfer is not a great business. I’m very curious to see what CX’s revenue model looks like.. At one level I do laugh.. just 5 years ago, the only top 5 Bank to allow online transfers out of the bank was BAC. I ran online and payment services at Wachovia (now part of WFC) which included all the online payment operations. The other bank retail heads were very reluctant to launch online transfers because of the risk of deposit run off.. or rate hopping. … wow have things changed.
Every year the banks delayed this service was another year that PayPal could develop a directory of mobile phone numbers, e-mail addresses and ACH information… this is the real battle… retail payments are a terrible business when viewed as a stand alone product.. but are essential to retail banking. (See Banks will win in Payments).
The only “cons” I have for ClearXchange are:
- It involves a technology build.. and clearly Chase and Cashedge have already built these functions. The banks should have gotten together and bought Cashedge.. particularly since BAC is Cashedge’s biggest customer.. they could have been running with this for 2 years
- The structure. Why not put this in The Clearing House? or Early Warning Services? another bank owned consortium does not make sense given their charter unless they plan on involving non-banks
- BAC, JPM, WFC.. will you please walk away from Visa Money Transfer.. they are attempting to walk all over what you are building here. My guess is that your Visa relationship managers are not talking to your P2P teams..